前言:
由于前段时间网鼎杯一道Android题目中用了这个,具有一定研究价值,便做一个壳的实现分析
https://github.com/luoyesiqiu/dpt-shell
其实这个是一个假的抽取壳,虽然函数抽取壳确实是将dex文件中的函数代码给nop,然后在运行时再把字节码给填回,但是不会填回内存中原dex位置,是填回内存中的一个解析后的结构体,比如梆梆加固,普通的工具是dump不到dex的。
虽然但是,能写出这个的也足以说明作者对Android的了解。即使作者也有howtowork文档去解释如何实现的,但是很多都被省略掉,这里做个源码分析,许多抽取壳也有类似的操作。
proccessor模块-源码分析
项目结构这里就不再说了,作者已经给出:https://github.com/luoyesiqiu/dpt-shell/blob/main/doc/HowItWorks.md
我们对照着项目结构对源码进行分析
主要是proccessor和shell两个部分
我们先分析可以将普通apk处理成加壳apk的proccessor模块
代码在dpt\src\main\java\com\luoye\dpt文件夹中
从Dpt.java开始分析
准备工作
-
读取命令行参数,获取我们电脑上的apk路径,并创建新的加壳apk文件路径
```java
private static void usage(){
System.err.println("Usage:\n\tjava -jar dpt.jar [--log] <ApkFile>");
}private static void processApk(String apkPath){ if(!new File("shell-files").exists()) { System.err.println("Cannot find shell files!"); return; } File apkFile = new File(apkPath); String apkFileName = apkFile.getName(); //获取apk名称 String currentDir = new File(".").getAbsolutePath(); // 当前命令行所在的目录 if (currentDir.endsWith("/.")){ currentDir = currentDir.substring(0, currentDir.lastIndexOf("/.")); } String output = FileUtils.getNewFileName(apkFileName,"signed");//新建output文件名 System.err.println("output: " + output); File outputFile = new File(currentDir, output);//创建一个File对象并获取其父文件夹路径 String outputApkFileParentPath = outputFile.getParent();```
-
获取工作目录径dptOut的绝对路径并将apk解压到工作目录
java String apkMainProcessPath = ApkUtils.getWorkspaceDir().getAbsolutePath(); System.out.println("Apk main process path: " + apkMainProcessPath); ApkUtils.extract(apkPath,apkMainProcessPath);//将apk解压到工作目录 -
解析AndroidManifest.xml获取packageName
getPackageName调用了getValue(file,"manifest","android","package");,然后getValue中利用pxb.android.axml.AxmlParser获取了manifest标签内命名空间为android的package属性的值,也就是存放我们包名的地方
java Global.packageName = ManifestUtils.getPackageName(apkMainProcessPath + File.separator + "AndroidManifest.xml");(重点)解析dex代码存入文件, 生成新的代码被nop了的dex
//从解压的apk工作目录下获取各个dex里面的代码存放到OoooooOooo文件中, 且创建了方法的code被填写为了nop的dex
ApkUtils.extractDexCode(apkMainProcessPath);
获取解压后的工作目录下的所有dex文件并遍历,调用 DexUtils.extractAllMethods,返回dex代码List<Instruction>,一个Instruction的List,其实一个Instruction就是dex中一个方法解析后存放的对象,不理解随时回去看这几个类
public static void extractDexCode(String apkOutDir){
List<File> dexFiles = getDexFiles(apkOutDir);//获取工作目录下所有的dex文件
List<List<Instruction>> instructionList = new ArrayList<>();
String appNameNew = "OoooooOooo";
String dataOutputPath = getOutAssetsDir(apkOutDir).getAbsolutePath() + File.separator + appNameNew; //OoooooOooo文件
for(File dexFile : dexFiles) {//遍历dex文件
String newName = dexFile.getName().endsWith(".dex") ? dexFile.getName().replaceAll("\\.dex$", "_tmp.dex") : "_tmp.dex";
File dexFileNew = new File(dexFile.getParent(), newName);
//抽取dex的代码, 一个Instruction存放一个方法的code, 返回的ret Instruction数组存放了该dex的方法的code, 并创建了新的被填入了nop的dex
List<Instruction> ret = DexUtils.extractAllMethods(dexFile, dexFileNew);
instructionList.add(ret);
//更新dex的hash
File dexFileRightHashes = new File(dexFile.getParent(),FileUtils.getNewFileName(dexFile.getName(),"new"));
DexUtils.writeHashes(dexFileNew,dexFileRightHashes);
dexFile.delete();
dexFileNew.delete();
dexFileRightHashes.renameTo(dexFile);
}
MultiDexCode multiDexCode = MultiDexCodeUtils.makeMultiDexCode(instructionList);//生成MultiDexCode结构存放所有dex的原本的code(这里是直接存放的代码, 我们其实可以将其加密之后存放)
MultiDexCodeUtils.writeMultiDexCode(dataOutputPath,multiDexCode);//将MultiDexCode结构写入到OoooooOooo文件中
}
接下来我们分析DexUtils.extractAllMethods,这个函数的作用很重要,也就是利用com.android.dex.Dex来解析dex文件,得到dex原本的各个方法的代码,一个方法对应一个解析后的Instruction对象,并且创建新的dex,将指令nop掉,后面会使用这个dex重新打包
public static List<Instruction> extractAllMethods(File dexFile, File outDexFile) {
List<Instruction> instructionList = new ArrayList<>(); //方法结构体 数组
Dex dex = null;
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null;
byte[] dexData = IoUtils.readFile(dexFile.getAbsolutePath());
IoUtils.writeFile(outDexFile.getAbsolutePath(),dexData);//将原本代码先write到新的outDexFile
try {
dex = new Dex(dexFile);//利用com.android.dex.Dex来解析
randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(outDexFile, "rw");
Iterable<ClassDef> classDefs = dex.classDefs();//获取dex中的全部类
for (ClassDef classDef : classDefs) { //遍历dex文件中的类
boolean skip = false;
//跳过系统类(上面的excludeRule中定义的不抽取的类的规则)
for(String rule : excludeRule){
if(classDef.toString().matches(rule)){
skip = true;
break;
}
}
if(skip){
continue;
}
if(classDef.getClassDataOffset() == 0){//获取类数据偏移
String log = String.format("class '%s' data offset is zero",classDef.toString());
logger.warn(log);
continue;
}
ClassData classData = dex.readClassData(classDef);//获取class数据
String className = dex.typeNames().get(classDef.getTypeIndex());
String humanizeTypeName = TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className);
ClassData.Method[] directMethods = classData.getDirectMethods();
ClassData.Method[] virtualMethods = classData.getVirtualMethods();
for (ClassData.Method method : directMethods) {//遍历directMethods
Instruction instruction = extractMethod(dex,randomAccessFile,classDef,method);
if(instruction != null) {
instructionList.add(instruction);
}
}
for (ClassData.Method method : virtualMethods) {//遍历virtualMethods
Instruction instruction = extractMethod(dex, randomAccessFile,classDef, method);
if(instruction != null) {
instructionList.add(instruction);
}
}
processedClassList.add(humanizeTypeName);
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
IoUtils.close(randomAccessFile);
}
return instructionList;
}
extractMethod方法(看我的注释进行理解)
private static Instruction extractMethod(Dex dex ,RandomAccessFile outRandomAccessFile,ClassDef classDef,ClassData.Method method)
throws Exception{
String returnTypeName = dex.typeNames().get(dex.protoIds().get(dex.methodIds().get(method.getMethodIndex()).getProtoIndex()).getReturnTypeIndex());//获取返回值类型
String methodName = dex.strings().get(dex.methodIds().get(method.getMethodIndex()).getNameIndex());
String className = dex.typeNames().get(classDef.getTypeIndex());
//native函数,abstract函数的codeoffset为0
if(method.getCodeOffset() == 0){
String log = String.format("method code offset is zero,name = %s.%s , returnType = %s",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName));
logger.warn(log);
return null;
}
Instruction instruction = new Instruction();//创建一个instruction的类来保存方法代码
//16 = registers_size + ins_size + outs_size + tries_size + debug_info_off + insns_size
int insnsOffset = method.getCodeOffset() + 16;//方法的ins是从偏移16开始的
Code code = dex.readCode(method);//读取方法的code
//容错处理
if(code.getInstructions().length == 0){
String log = String.format("method has no code,name = %s.%s , returnType = %s",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName));
logger.warn(log);
return null;
}
int insnsCapacity = code.getInstructions().length;//获取指令长度
//insns容量不足以存放return语句,跳过
byte[] returnByteCodes = getReturnByteCodes(returnTypeName);//根据类型缩写获取return语句的code
if(insnsCapacity * 2 < returnByteCodes.length){
logger.warn("The capacity of insns is not enough to store the return statement. {}.{}() ClassIndex = {}-> {} insnsCapacity = {}byte(s) but returnByteCodes = {}byte(s)",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
classDef.getTypeIndex(),
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName),
insnsCapacity * 2,
returnByteCodes.length);
return null;
}
instruction.setOffsetOfDex(insnsOffset);
//这里的MethodIndex对应method_ids区的索引
instruction.setMethodIndex(method.getMethodIndex());
//注意:这里是数组的大小
instruction.setInstructionDataSize(insnsCapacity * 2);
byte[] byteCode = new byte[insnsCapacity * 2];
//循环读取原先方法的指令写入到bytecode数组中, 然后填入nop到新dex中
for (int i = 0; i < insnsCapacity; i++) {
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset + (i * 2));
byteCode[i * 2] = outRandomAccessFile.readByte();
byteCode[i * 2 + 1] = outRandomAccessFile.readByte();
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset + (i * 2));
outRandomAccessFile.writeShort(0);//写入两条nop
}
instruction.setInstructionsData(byteCode);//将原先的code填入instruction结构体
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset);
//写入return语句
outRandomAccessFile.write(returnByteCodes);
return instruction;
}
其实他这里是直接存放了原先dex的code,没有加密,我们可以加密存放,增加安全性,避免能直接从assets/OoooooOooo文件中把本来的dex code拿到
AndroidManifest.xml修改及其修改后的影响
主要是修改了两个地方,也有较多其他壳会修改这个andoroid:name和android:appComponentFactory,写了下application里面android:name的影响以及android:appComponentFactory是怎么被获取到的分析
//获取AndroidManifest.xml里的application标签内的android:name属性保存到**app_name**文件中
ApkUtils.saveApplicationName(apkMainProcessPath);
//写入com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyApplication到application标签内的android:name属性中
ApkUtils.writeProxyAppName(apkMainProcessPath);
//获取AndroidManifest.xml里的android:appComponentFactory属性保存到**app_acf**文件中
ApkUtils.saveAppComponentFactory(apkMainProcessPath);
//写入com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyComponentFactory到application标签内的android:appComponentFactory属性
ApkUtils.writeProxyComponentFactoryName(apkMainProcessPath);
application中的android:name属性指定了当应用程序进程开始时,该类在所有应用程序组件之前被实例化。
AppComponentFactory理解:原本代码
public class AppComponentFactory {
//提供类加载器
public @NonNull ClassLoader instantiateClassLoader(@NonNull ClassLoader cl,
@NonNull ApplicationInfo aInfo) {
return cl;
}
//创建Application
public @NonNull Application instantiateApplication(@NonNull ClassLoader cl,
@NonNull String className)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (Application) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
//Activity组件
public @NonNull Activity instantiateActivity(@NonNull ClassLoader cl, @NonNull String className,
@Nullable Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (Activity) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
//BroadcastReceiver组件
public @NonNull BroadcastReceiver instantiateReceiver(@NonNull ClassLoader cl,
@NonNull String className, @Nullable Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (BroadcastReceiver) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
//server组件
public @NonNull Service instantiateService(@NonNull ClassLoader cl,
@NonNull String className, @Nullable Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (Service) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
//ContentProvider组件
public @NonNull ContentProvider instantiateProvider(@NonNull ClassLoader cl,
@NonNull String className)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (ContentProvider) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
public static final AppComponentFactory DEFAULT = new AppComponentFactory();
}
这个类主要有六个方法和一个指向自己的变量,六个方法包括一个方法是提供类加载器,一个是创建Application,例外四个是创建Android的四大组件。
只要在application中配置了android:appComponentFactory,系统在创建Application和四大组件时就会调用到这里配置的这个类,如果没有配置,那么就会直接使用上面类内部定义的DEFAULT变量。
在android启动流程中,ActivityThread.main()是进入app的大门,在进程创建后会在其中调用ActivityThread的attach(),接着就会调用到ActivityManagerService.attachApplication()—>attachApplicationLocked(),在attachApplicationLocked()又会调用到ActivityThread.ApplicationThread.bindApplicaiton(),其实这个主要就是赋值,然后通过handler发送消息,最终调用到的是ActivityThread.handleBindApplication
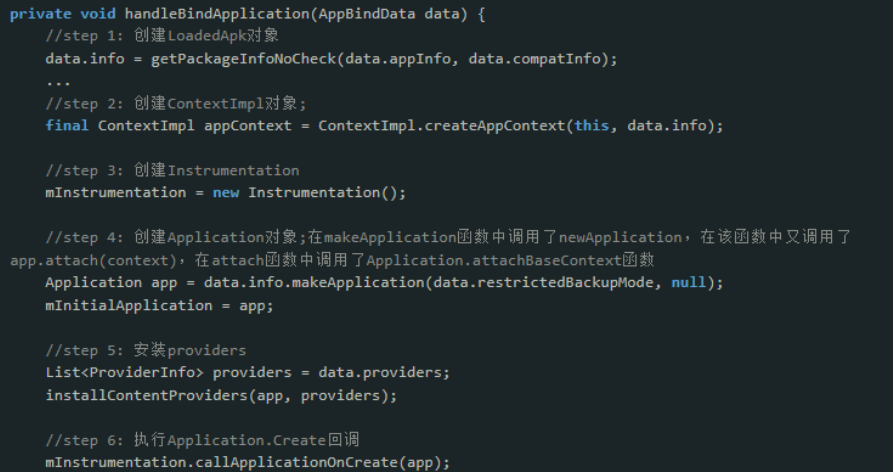
在step4,调用了makeApplication,里面又调用了newApplication
public Application newApplication(ClassLoader cl, String className, Context context)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
Application app = getFactory(context.getPackageName())
.instantiateApplication(cl, className);
app.attach(context);
return app;
}
private AppComponentFactory getFactory(String pkg) {
if (pkg == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "No pkg specified, disabling AppComponentFactory");
return AppComponentFactory.DEFAULT;
}
if (mThread == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Uninitialized ActivityThread, likely app-created Instrumentation,"
+ " disabling AppComponentFactory", new Throwable());
return AppComponentFactory.DEFAULT;
}
LoadedApk apk = mThread.peekPackageInfo(pkg, true);
// This is in the case of starting up "android".
if (apk == null) apk = mThread.getSystemContext().mPackageInfo;
return apk.getAppFactory();
}
调用getFactory获取AppComponentFactory实例化Application,然后调用Application的attach()方法,进而调用Application的attachBaseContext(),这也说明attachBaseContext()比ContentProvide先执行,这里我们继续看AppComponentFactory的获取LoadedApk.getAppFactory():
public AppComponentFactory getAppFactory() {
return mAppComponentFactory;
}
只是简单的返回mAppComponentFactory属性,因为AppComponentFactory的创建是在LoadedApk的构造函数中调用createAppFactory()创建的
private AppComponentFactory createAppFactory(ApplicationInfo appInfo, ClassLoader cl) {
if (appInfo.appComponentFactory != null && cl != null) {
try {
return (AppComponentFactory)
cl.loadClass(appInfo.appComponentFactory).newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unable to instantiate appComponentFactory", e);
}
}
return AppComponentFactory.DEFAULT;
}
这里就获取了我们在Manifest中配置的AppComponentFactory。
然后上面填写的com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyApplication和com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyComponentFactory我们一会儿再仔细分析(这两个类都在后面会打包进新apk的代理dex中)
代理dex添加、删除meta-data、壳lib支持添加、重打包及重签名
//往apk中添加代理dex(将项目文件shell-files/dex/classes.dex写入到apk目录中)
ApkUtils.addProxyDex(apkMainProcessPath);
//删除meta-data
ApkUtils.deleteMetaData(apkMainProcessPath);
//把shell-libs(壳的so文件)也copy到apk目录中
ApkUtils.copyShellLibs(apkMainProcessPath, new File(outputApkFileParentPath,"shell-files/libs"));
//重打包以及签名
new BuildAndSignApkTask(false, apkMainProcessPath, output).run();
//删除工作目录
File apkMainProcessFile = new File(apkMainProcessPath);
if (apkMainProcessFile.exists()) {
FileUtils.deleteRecurse(apkMainProcessFile);
}
代理dex结构:
shell模块-源码分析
我们先来分析代理实现(就是上面往apk中添加的那个dex),也就是
android:appComponentFactory="com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyComponentFactory"
android:name="com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyApplication"
其实主要是com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyApplication
首先我们要知道在ActivityThread启动流程中,handleBindApplication会调用makeApplication,然后makeApplication又会调用newApplication,而newApplication就是调用getFactory获取AppComponentFactory实例化Application,然后调用Application的attach()方法,进而调用Application的attachBaseContext(),然后回到handleBindApplication进入callApplicationOnCreate()函数就执行了Application.onCreate()方法
而这个项目的com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyApplication就是Override了OnCreate方法和attachBaseContext方法
ProxyApplication-attachBaseContext重写解析
我们先看attachBaseContext
先调用原本的(父类的)attachBaseContext,然后调用native的init_app函数,并重新加载了一次dex,将新的dex也添加到本来的classload的DexPathList obj中, 以便classloader从中加载类
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);//先调用原本的attachBaseContext
Log.d(TAG,"dpt attachBaseContext");
Log.d(TAG,"attachBaseContext classloader = " + base.getClassLoader());
if(!initialized) {
Log.d(TAG,"ProxyApplication init");//ProxyApplication初始化
//调用native的init_app函数
//init_app函数(将zip open后mmap到内存中, 然后获取加载到内存中apk的assets/OoooooOooo文件的指针, 然后调用readCodeItem将这个MultiDexCode结构体解析出来获得各个dex的代码, 然后添加到dexMap中)
JniBridge.ia(base,base.getClassLoader());
//获取原本的ClassLoader
ClassLoader oldClassLoader = base.getClassLoader();
//获取新的ClassLoader, 重新加载一次dex
//dex在App启动的时候已经被加载过一次了,但是,我们为什么还要再加载一次?因为系统加载的dex是以只读方式加载的,我们没办法去修改那一部分的内存
//而且App的dex加载早于我们Application的启动,这样,我们的代码根本没法感知到,所以我们要重新加载dex
//loadDex, 实际上就是查找了下路径然后然后调用super实例化了PathClassLoader并返回
ClassLoader shellClassLoader = ShellClassLoader.loadDex(base);
//然后利用获取到的shellClassLoader, 将新的dex也添加到本来的classload的DexPathList obj中, 以便classloader从中加载类
JniBridge.mde(oldClassLoader,shellClassLoader);
initialized = true;
}
}
我们先看init_app,其实上面我已经注释的很详细了,就是将zip open后mmap到内存中, 然后获取加载到内存中apk的assets/OoooooOooo文件的指针, 然后调用readCodeItem将这个MultiDexCode结构体解析出来获得各个dex的代码, 然后添加到dexMap中,dexMap后面回填代码的时候会被用到
其实native定义的CodeItem类和我们的Instruction类相对应,成员都是一样的
//在dex中的偏移
private int offsetOfDex;
//对应dex中的method_idx
private int methodIndex;
//instructionsData数组的长度
private int instructionDataSize;
//指令数据
private byte[] instructionsData;
uint32_t mMethodIdx; //和上面相同
uint32_t mOffsetDex;
uint32_t mInsnsSize;
uint8_t* mInsns;
ProxyApplication-onCreate重写解析(hook点)
先调用本身的onCreate,然后调用了两个native的函数,callRealApplicationAttach和callRealApplicationOnCreate
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();//先调用本身的onCreate
Log.d(TAG, "dpt onCreate");
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate() classLoader = " + getApplicationContext().getClassLoader());
//读取app真实名称
String realApplicationName = FileUtils.readAppName(getApplicationContext());
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(realApplicationName)) {//字符串非空会进入
//调用native的callRealApplicationAttach函数去调用原始apk Application类的attach方法
JniBridge.craa(getApplicationContext(), realApplicationName);
}
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(realApplicationName)) {
JniBridge.craoc(realApplicationName);
//调用native的callRealApplicationOnCreate函数调用原始apk Application类的onCreate方法
}
}
craa和craoc中都会调用getApplicationInstance, 然后里面会调用_init函数, 也就是去调用dpt_hook函数
extern "C" void _init(void)
{
DLOGI("_init!");
dpt_hook();
}
void dpt_hook()
{
bytehook_init(BYTEHOOK_MODE_AUTOMATIC, false);
g_sdkLevel = android_get_device_api_level(); //获取sdklevel
hook_mmap(); //修改mmap以便在我们加载dex后能够修改dex的属性为可写
hook_ClassLinker_LoadMethod(); // hook loadmethod以便将我们存放到dexmap中的代码写回到内存中的dex原本位置(里面也调用了changeDexProtect, 利用mprotect来修改了dex权限为可读写),一次回填一个method
hook_GetOatDexFile();
}
重写了AppComponentFactory类
反正六个方法里面都是getTargetAppComponentFactory获取自身这个ProxyComponentFactory类并实例化,并设置到返回sAppComponentFactory静态变量且返回这个对象,然后方法里面回去判断是否为null,如果≠null就重新调用本类的本方法,否则就调用super AppComponentFactory的本方法
总之就是为了尽早初始化,不太重要
package com.luoyesiqiu.shell;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AppComponentFactory;
import android.app.Application;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.ContentProvider;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.ApplicationInfo;
import android.util.Log;
import com.luoye.dpt.ThisApplication;
import com.luoyesiqiu.shell.util.ShellClassLoader;
import com.luoyesiqiu.shell.util.StringUtils;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.annotation.RequiresApi;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@RequiresApi(api = 28)
public class ProxyComponentFactory extends AppComponentFactory {
private static final String TAG = "dpt " + ProxyComponentFactory.class.getSimpleName();
private static AppComponentFactory sAppComponentFactory;
//readAppComponentFactory, 读取我们设置的AppComponentFactory属性的值
//也就是com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyComponentFactory
private String getTargetClassName(ClassLoader classLoader){
return JniBridge.rcf(classLoader);
}
//加载自身类,并实例化类,从此系统中有了两个类
private AppComponentFactory getTargetAppComponentFactory(ClassLoader classLoader){
if(sAppComponentFactory == null){
String targetClassName = getTargetClassName(classLoader);//获取到com.luoyesiqiu.shell.ProxyComponentFactory
Log.d(TAG,"targetClassName = " + targetClassName);
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(targetClassName)) {
try {//用目标类名创建一个新的AppComponentFactory对象并返回
sAppComponentFactory = (AppComponentFactory) Class.forName(targetClassName).newInstance();
return sAppComponentFactory;
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
return sAppComponentFactory;
}
private void init(ClassLoader cl){
if(!ProxyApplication.initialized){
ProxyApplication.initialized = true;
JniBridge.ia(null,cl);//init app
String apkPath = JniBridge.gap(cl);//getApkPath
ClassLoader classLoader = ShellClassLoader.loadDex(apkPath);
//将新的dex也添加到本来的classload的DexPathList obj中, 以便classloader从中加载类
JniBridge.mde(cl,classLoader);
Log.d(TAG,"ProxyComponentFactory init() classLoader = " + classLoader);
}
}
//重写Activity
@Override
public Activity instantiateActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className, Intent intent) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Log.d(TAG, "instantiateActivity() called with: cl = [" + cl + "], className = [" + className + "], intent = [" + intent + "]");
AppComponentFactory targetAppComponentFactory = getTargetAppComponentFactory(cl);
if(targetAppComponentFactory != null) {//如果是壳程序
try {
Method method = AppComponentFactory.class.getDeclaredMethod("instantiateActivity", ClassLoader.class, String.class, Intent.class);
return (Activity) method.invoke(targetAppComponentFactory, cl, className, intent);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
return super.instantiateActivity(cl, className, intent);//不是壳程序
}
//重写Application的加载
@Override
public Application instantiateApplication(ClassLoader cl, String className) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Log.d(TAG, "instantiateApplication() called with: cl = [" + cl + "], className = [" + className + "]");
init(cl);
AppComponentFactory targetAppComponentFactory = getTargetAppComponentFactory(cl);
if(targetAppComponentFactory != null) {//如果是壳程序
try {
Method method = AppComponentFactory.class.getDeclaredMethod("instantiateApplication", ClassLoader.class, String.class);
return (Application) method.invoke(targetAppComponentFactory, cl, className);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
return super.instantiateApplication(cl, ThisApplication.class.getName());//如果不是
}
//重写获取类加载器的instantiateClassLoader
@Override
public ClassLoader instantiateClassLoader(ClassLoader cl, ApplicationInfo aInfo) {
Log.d(TAG, "instantiateClassLoader() called with: cl = [" + cl + "], aInfo = [" + aInfo + "]");
init(cl);
AppComponentFactory targetAppComponentFactory = getTargetAppComponentFactory(cl);
//获取本类自身实例化后的对象
if(targetAppComponentFactory != null) {
try {
Method method = AppComponentFactory.class.getDeclaredMethod("instantiateClassLoader", ClassLoader.class, ApplicationInfo.class);
return (ClassLoader) method.invoke(targetAppComponentFactory, cl, aInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
return super.instantiateClassLoader(cl, aInfo);
}
@Override
public BroadcastReceiver instantiateReceiver(ClassLoader cl, String className, Intent intent) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Log.d(TAG, "instantiateReceiver() called with: cl = [" + cl + "], className = [" + className + "], intent = [" + intent + "]");
AppComponentFactory targetAppComponentFactory = getTargetAppComponentFactory(cl);
if(targetAppComponentFactory != null) {
try {
Method method = AppComponentFactory.class.getDeclaredMethod("instantiateReceiver", ClassLoader.class, String.class, Intent.class);
return (BroadcastReceiver) method.invoke(targetAppComponentFactory, cl, className, intent);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
return super.instantiateReceiver(cl, className, intent);
}
@Override
public Service instantiateService(ClassLoader cl, String className, Intent intent) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Log.d(TAG, "instantiateService() called with: cl = [" + cl + "], className = [" + className + "], intent = [" + intent + "]");
AppComponentFactory targetAppComponentFactory = getTargetAppComponentFactory(cl);
if(targetAppComponentFactory != null) {
try {
Method method = AppComponentFactory.class.getDeclaredMethod("instantiateReceiver", ClassLoader.class, String.class, Intent.class);
return (Service) method.invoke(targetAppComponentFactory, cl, className, intent);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
return super.instantiateService(cl, className, intent);
}
@NonNull
@Override
public ContentProvider instantiateProvider(@NonNull ClassLoader cl, @NonNull String className) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Log.d(TAG, "instantiateProvider() called with: cl = [" + cl + "], className = [" + className + "]");
AppComponentFactory targetAppComponentFactory = getTargetAppComponentFactory(cl);
if(targetAppComponentFactory != null) {
try {
Method method = AppComponentFactory.class.getDeclaredMethod("instantiateProvider", ClassLoader.class, String.class);
return (ContentProvider) method.invoke(targetAppComponentFactory, cl, className);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
return super.instantiateProvider(cl, className);
}
}
脱壳处理(案例:2022网鼎杯-whereiscode)
方法1:frida-dexdump直接dump以及能直接dump的原因
原因:frida-dexdump这个工具是直接暴力搜索的内存,这个壳因为是将解析出来的code hook的loadmethod填回了内存中dex的原位,所以能直接dump到,所以为什么说它不是真的抽取壳
记得使用最新版的frida-dexdump,添加-d(deep search)参数
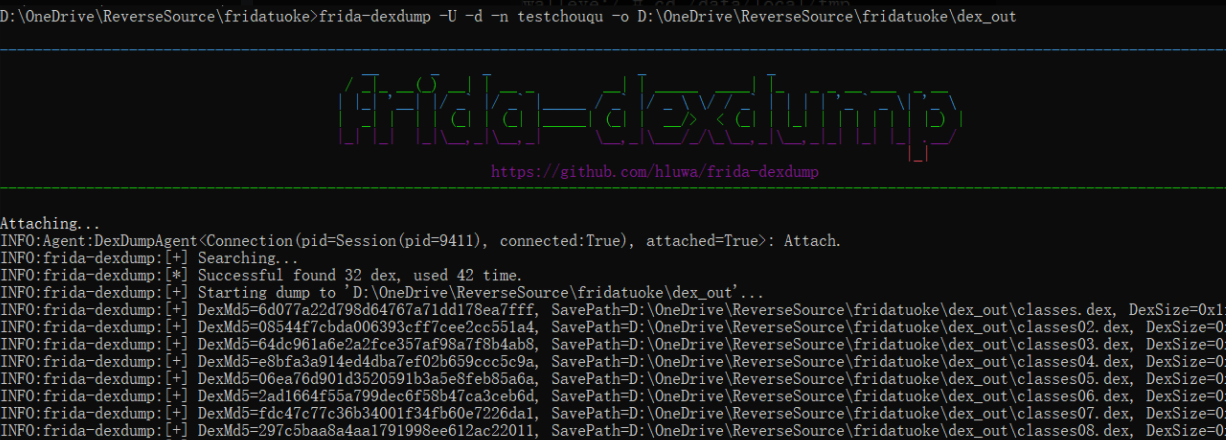
就能看见关键的check代码
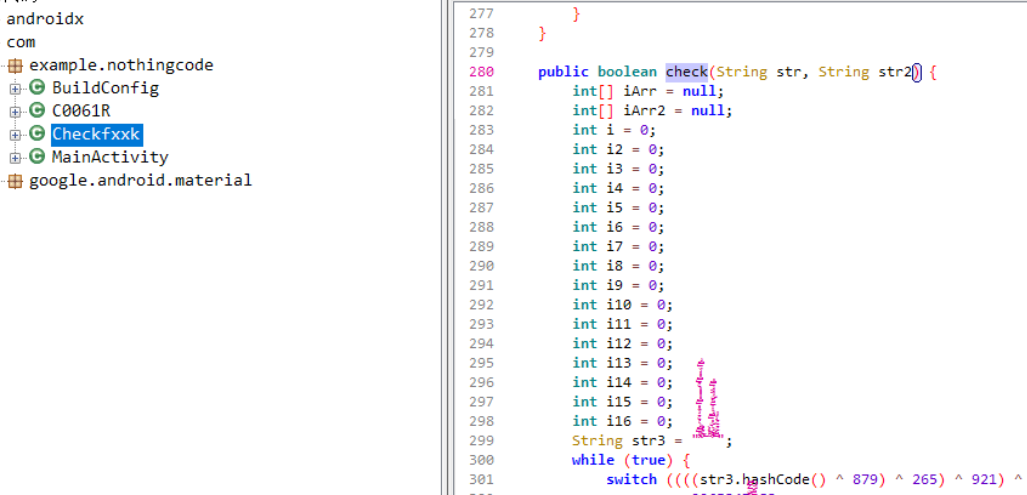
方法2:静态解析assets/OoooooOooo文件
我们分析了源码之后是知道它是怎么提取的代码,以及各种类的结构,实际上这个文件就是MultiDexCode类的对象,我们按照它的代码写个解析即可
仔细看MultiDexCodeUtils.java,尤其是writeMultiDexCode,就是作者将code写入到文件中的操作,我们根据这个把oo..文件解析出来提取到各个dex的code(都恢复成那个List<Instruction> instructions类型)
public class MultiDexCodeUtils {
/**
* 生成MultiDexCode结构
*/
public static MultiDexCode makeMultiDexCode(List<List<Instruction>> multiDexInsns){
int fileOffset = 0;
MultiDexCode multiDexCode = new MultiDexCode();
multiDexCode.setVersion(Const.MULTI_DEX_CODE_VERSION);
fileOffset += 2;
multiDexCode.setDexCount((short) multiDexInsns.size());//通过二维数组的长度判断dex个数
fileOffset += 2;
List<Integer> dexCodeIndex = new ArrayList<>();
multiDexCode.setDexCodesIndex(dexCodeIndex);
fileOffset += 4 * multiDexInsns.size();
List<DexCode> dexCodeList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> insnsIndexList = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<Instruction> insns : multiDexInsns) {
System.out.println("DexCode offset = " + fileOffset);
dexCodeIndex.add(fileOffset);
DexCode dexCode = new DexCode();
dexCode.setMethodCount((short)insns.size());
fileOffset += 2;
dexCode.setInsns(insns);
insnsIndexList.add(fileOffset);
dexCode.setInsnsIndex(insnsIndexList);
for (Instruction ins : insns) {
fileOffset += 4; //Instruction.offsetOfDex
fileOffset += 4; //Instruction.methodIndex
fileOffset += 4; //Instruction.instructionDataSize
fileOffset += ins.getInstructionsData().length; //Instruction.instructionsData
}
dexCodeList.add(dexCode);
}
System.out.println("fileOffset = " + fileOffset);
multiDexCode.setDexCodes(dexCodeList);
return multiDexCode;
}
/**
* 写入MultiDexCode结构
* @param multiDexCode MultiDexCode结构
*/
public static void writeMultiDexCode(String out, MultiDexCode multiDexCode){
if(multiDexCode.getDexCodes().isEmpty()){
return;
}
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null;
try {
randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(out, "rw");
//写入版本号(short)
randomAccessFile.write(Endian.makeLittleEndian(multiDexCode.getVersion()));
//写入dex数量(short)
randomAccessFile.write(Endian.makeLittleEndian(multiDexCode.getDexCount()));
//写入每个dex在文件中的位置
for (Integer dexCodesIndex : multiDexCode.getDexCodesIndex()) {
//DexCode的索引,List长度为dex的数量 private List<Integer> dexCodesIndex;
randomAccessFile.write(Endian.makeLittleEndian(dexCodesIndex));
}
//写入每个dex的数据
for (DexCode dexCode : multiDexCode.getDexCodes()) {
List<Instruction> insns = dexCode.getInsns();
int methodCount = dexCode.getMethodCount() & 0xFFFF;
System.out.println("insns item count:" + insns.size() + ",method count : " + methodCount);
//写入该dex的方法数
randomAccessFile.write(Endian.makeLittleEndian(dexCode.getMethodCount()));
for (int i = 0; i < insns.size(); i++) {//写入单个dex的方法代码(长度的话就读取4+4+4+1*getInstructionDataSize() )
Instruction instruction = insns.get(i);
randomAccessFile.write(Endian.makeLittleEndian(instruction.getMethodIndex()));
randomAccessFile.write(Endian.makeLittleEndian(instruction.getOffsetOfDex()));
randomAccessFile.write(Endian.makeLittleEndian(instruction.getInstructionDataSize()));
randomAccessFile.write(instruction.getInstructionsData());
}
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
IoUtils.close(randomAccessFile);
}
}
}
最后调用这个代码即可恢复
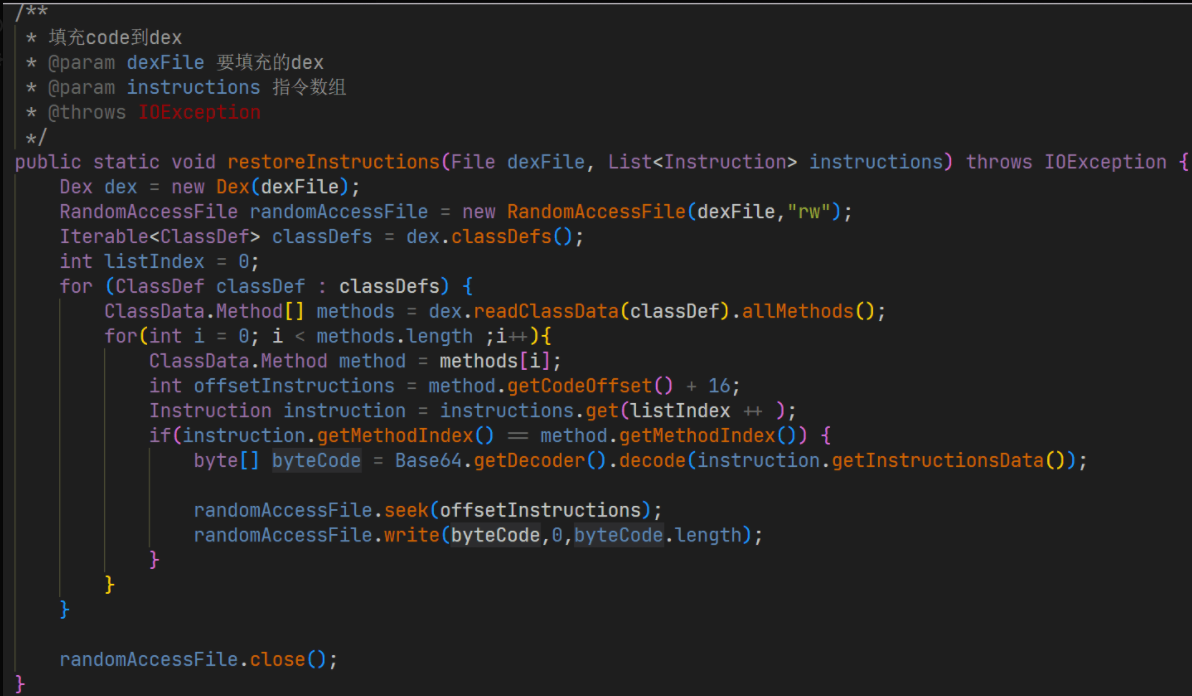
资料:
https://github.com/luoyesiqiu/dpt-shell
https://github.com/luoyesiqiu/dpt-shell/blob/main/doc/HowItWorks.md
https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-273293.htm#msg_header_h2_1
 跳跳糖
跳跳糖

