0x00 前言
近期的在看 pwn 的一些东西,发现无论是实际场景中,还是 CTF 中,堆的利用越来越多,又由于各种环境下堆的实现都不太一样,因此就让皂皂翻译这篇文章, 我也对本文作了润色修改,以飨读者。
原文:https://sploitfun.wordpress.com/2015/02/10/understanding-glibc-malloc/comment-page-1/
我一直在执着于堆的一些问题。比如以下几个
- 堆的内存怎样从内核中申请的?
- 怎样有效地进行内存管理?
- 堆内存是通过内核,库还是堆本身进行管理?
- 堆的一些相关问题能被利用吗?
虽然之前经常在想这些问题,但是光想并没有什么卵用。正好,最近我找到了点时间来好好思考这些问题。所以现在我就来分享一下这些知识的总结。此外,还有很多可用的内存分配器:
- dlmalloc - 通用分配器
- ptmallac2- glibc
- jemalloc - FreeBSD & Firefox
- tcmalloc - Google
- libumem - Solaris ...
每种内存分配器都说他们是最快的、可扩展并且具有高效的内存使用!!但是并非所有的分配器都适合我们自己的应用程序。内存消耗大的应用性能很大程度依赖于内存分配器的性能。本文中,我只讨论 "glibc malloc” 内存分配器。并希望今后能涉及到其他内存分配器的讨论。本文中为了更好的理解 ”glibc malloc”,我会联系它最近的源码来谈。好,下面系好你的安全带,我们开启探索 glibc malloc 的旅程!!
0x01 历史
历史:ptmalloc2来自于dlmalloc的分支。此后,添加线程支持并于 2006 年发布。正式发布后,patmalloc2 集成到 glibc 源码中。随着源码集成,代码修改便直接在 glibc malloc 源码里进行。因此 ptmalloc2 与 glibc 之间的 malloc 实现有很多不同。
系统调用:在之前的文章可见malloc的内部调用不是brk就是mmap系统调用。
线程化:在早期的 Linux 里,dlmalloc 被用做默认的内存分配器。但之后因为 ptmalloc2 添加了线程支持,ptmalloc2 成为了 Linux 默认内存分配器。线程支持可帮助提升内存分配器以及应用程序的性能。在 dlmalloc 里,当两个线程同时调用 malloc 时,只有一个线程能进入到临界段,因为这里的空闲列表数据结构是所有可用线程共用的。因此内存分配器要在多线程应用里耗费时间,从而导致性能降低。然而在 ptmalloc2 里,当两个线程同时调用 malloc 时,会立即分配内存。因为每个线程维护一个单独的堆分段,因此空闲列表数据结构正在维护的这些堆也是独立的。这种维护独立堆以及每一个线程享有空闲列表数据结构的行为被称为 Per Thread Arena。
0x02 示例:
/* Per thread arena example. */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
void* threadFunc(void* arg) {
printf("Before malloc in thread 1\n");
getchar();
char* addr = (char*) malloc(1000);
printf("After malloc and before free in thread 1\n");
getchar();
free(addr);
printf("After free in thread 1\n");
getchar();
}
int main() {
pthread_t t1;
void* s;
int ret;
char* addr;
printf("Welcome to per thread arena example::%d\n",getpid());
printf("Before malloc in main thread\n");
getchar();
addr = (char*) malloc(1000);
printf("After malloc and before free in main thread\n");
getchar();
free(addr);
printf("After free in main thread\n");
getchar();
ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, threadFunc, NULL);
if(ret)
{
printf("Thread creation error\n");
return -1;
}
ret = pthread_join(t1, &s);
if(ret)
{
printf("Thread join error\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
输出分析:
在主线程 malloc 之前:在以下输出里我们可以看到,由于 thread1 尚未创建,这里尚无堆分段,也没有线程栈。
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::6501
Before malloc in main thread
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc/6501/maps
08048000-08049000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
08049000-0804a000 r--p 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p 00001000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
b7e05000-b7e07000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
在主线程 malloc 之后: 在下面的输出里我们可以看到,堆正好被创建在数据段附近(0804b000-0806c000),这表明堆的空间是由调用高级别的中断所创建(即,使用brk系统调用)。还要注意的是,即使用户只发出了 1000 bytes 请求,就会创建132 KB大小的堆内存。这个堆内存的连续区域被称为「arena」。这个 arena 是由主线程创建,则被称为main arena。进一步的分配请求会继续使用这个 arena 直到arena 空闲空间耗尽。当 arena 耗尽空闲空间 时,它能在线程调用高级别的中断的位置时建立(调整建立开始块的size以包含额外空间之后)。类似地,arena 也能在 top chunk 有大量空闲空间时回收。
注:top chunk 是一个 arena 里最多的块。关于它的更多细节,请看以下 "Top Chunk" 部分
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::6501
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/lsploits/hof/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc/6501/maps
08048000-08049000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
08049000-0804a000 r--p 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p 00001000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
b7e05000-b7e07000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
在主线程 Free 之后: 在以下输出里我们可以看到,当分配内存区域被释放时,其后内存不会被立即释放给操作系统。分配内存区域(1000 bytes 大小)只释放给 "glibc malloc" 库,在这里的释放掉的 Chunk 会被添加到 main arenas 中(在 glibc malloc 里,freelist 这种数据结构被称为 bins 译者注:freelist 是一种单向链表)。此后当用户申请内存时,glibc malloc 不会从内核中获得新的堆内存,而是尽量在 bins 里找到一个空闲块(Free Chunk)。只有当没有空闲块存在时,glibc malloc 才会从继续内核中申请内存。
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::6501
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
After free in main thread
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/lsploits/hof/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc/6501/maps
08048000-08049000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
08049000-0804a000 r--p 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p 00001000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
b7e05000-b7e07000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
在线程1 malloc 之前:在以下输出中我们可以看到,这里没有 thread1 的堆但现在 thread1 的每一线程栈已被创建。
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::6501
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
After free in main thread
Before malloc in thread 1
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc/6501/maps
08048000-08049000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
08049000-0804a000 r--p 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p 00001000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
b7604000-b7605000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0
b7605000-b7e07000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [stack:6594]
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
在线程1 malloc 之后:在以下输出里我们可以看到,thread1 的堆被创建了。且在内存映射段区域出现(b7500000-b7521000 大小为 132 KB),这表明堆内存通过使用 mmap 系统调用而不是主线程(使用 sbrk)创建。这里再一次看到,即使用户只请求 1000 bytes,1MB 大小的堆内存还是会被映射到进程地址空间中。而1 MB以外只有 132KB 被设置有读写权限,并同时成为该线程的堆。这块内存(132KB)区域被称为thread arena。
注:当用户申请的内存大小超过 128KB( malloc(132*1024) )并且当一个 arena 里没有足够的空间来满足用户的请求时,内存是使用 mmap 系统调用来分配的(不使用 sbrk) 无论这个请求是来自于 main arena 还是 thread arena。
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::6501
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
After free in main thread
Before malloc in thread 1
After malloc and before free in thread 1
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc/6501/maps
08048000-08049000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
08049000-0804a000 r--p 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p 00001000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
b7500000-b7521000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
b7521000-b7600000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0
b7604000-b7605000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0
b7605000-b7e07000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [stack:6594]
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
在线程1 free 掉后:在以下输出我们可以看到,释放分配内存区域的过程中并不会把堆释放到操作系统。取而代之的是这块被分配的内存区域(1000 bytes 大小)还是被释放到了 "glibc malloc" 里,并将这个释放块添加到 thread arenas 的 bins 里。
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::6501
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
After free in main thread
Before malloc in thread 1
After malloc and before free in thread 1
After free in thread 1
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc/6501/maps
08048000-08049000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
08049000-0804a000 r--p 00000000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p 00001000 08:01 539625 /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
b7500000-b7521000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
b7521000-b7600000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0
b7604000-b7605000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0
b7605000-b7e07000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [stack:6594]
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
0x03 Arena
Arena的数量:在以上示例中,我们看到了主线程包含 main arena 同时 thread 1 包含了它自己的 thread arena。所以不论线程数量,在线程与 arena 之间可以有一对一的映射吗?当然没有。一个 arena 应用程序可以包含更多数量的线程(相较于 Cores 的数量),在这样的情况下,每个线程拥有一个 arena 显得有些不值。因此,应用程序的arena 数量的限制是基于系统里现有的 Cores 的数量。
For 32 bit systems:
Number of arena = 2 * number of cores.
For 64 bit systems:
Number of arena = 8 * number of cores.
0x04 Multiple Arena :
示例:我们来看一个多线程应用(4线程 ---||- 主线程 + 3个用户线程)在一个单核的 32 位系统上运行。这里线程数量(4)> 2 * 核心数量(2)。因此,"glibc malloc" 认定 Multiple Arena 被所有可用进程共享。但它是怎样共享的呢?
当主线程,第一次调用 malloc 时,在没有任何竞争的情况下,已经创建了main arena。
当 thread 1 和 thread 2 第一次调用 malloc 时,会为这些线程创建一个新的 arena并且是在无任何竞争的情况下被使用。直到所有线程和 arena 有一对一映射时。
当 thread 3 第一次调用 malloc 时, arena 限制的数量被算出。这里超过了 arena 数量的限制,因此尝试重用现存的 arena (main arena 或 arena 1 或 arena 2)
重用:
一旦遍历了所有可用的 arena,就会尽量去锁定可用的 arena。
如果锁定成功(我们假设说 main arena 被锁定成功),就向用户返回该 arena。
如果没有 arena 是空闲的,请看接下来的arena代码区。
现在当 thread 3 第二次调用 malloc 时,malloc 会尽量使用上次访问的 arena(main arena)。如果 main arena 是空闲的, thread 3 会一直使用该 arena 并屏蔽其他线程的申请直到 main arena 被释放。 main arena 就是如此这般在主线程和 thread 3 间共享。
0x05 Multiple Heaps:
在 “glibc malloc”源代码里主要发现以下三种数据结构:
heap_info – 堆头 – 单个 thread arena 有多个堆。每个堆有它自己的头。为什么需要多个堆?每个 thread arena 开始都只有一个堆,但当这个堆耗尽空间时,新的堆(并不连续的)能 mmap 到这个 arena 里。
malloc_state – Arena 头 – 单个 thread arena 有多个堆,但是对于所有这些堆来说,只存在一个 arena 头。arena 头 包含 bins、top chunk、最后剩余块……
malloc_chunk – 块头 – 一个堆基于用户请求被分为很多块。每个块有它自己的块头。
注:
Main arena 没有多重堆,因此没有 heap_info 结构。当main arena 耗尽空间时,sbrk 堆被扩展(连续区域)直到它转储到内存映射分段中。
不像 thread arena,main arena 的 Arena 头不是 sbrk 堆分段的一部分。它是一个全局变量,因此可以在 libc 里找到它以及数据分段。
main arena 和 thread arena 的形象化视图(单个堆分段):
thread arena 的形象化视图(多个堆分段):
Chunk :在堆里的块可以是以下几种类型中的一种:
- Allocated chunk 分配后的块
- Free chunk 空闲块
- Top chunk 开始块
- Last Remainder chunk 最后剩余块
0x06 Allocated Chunk:
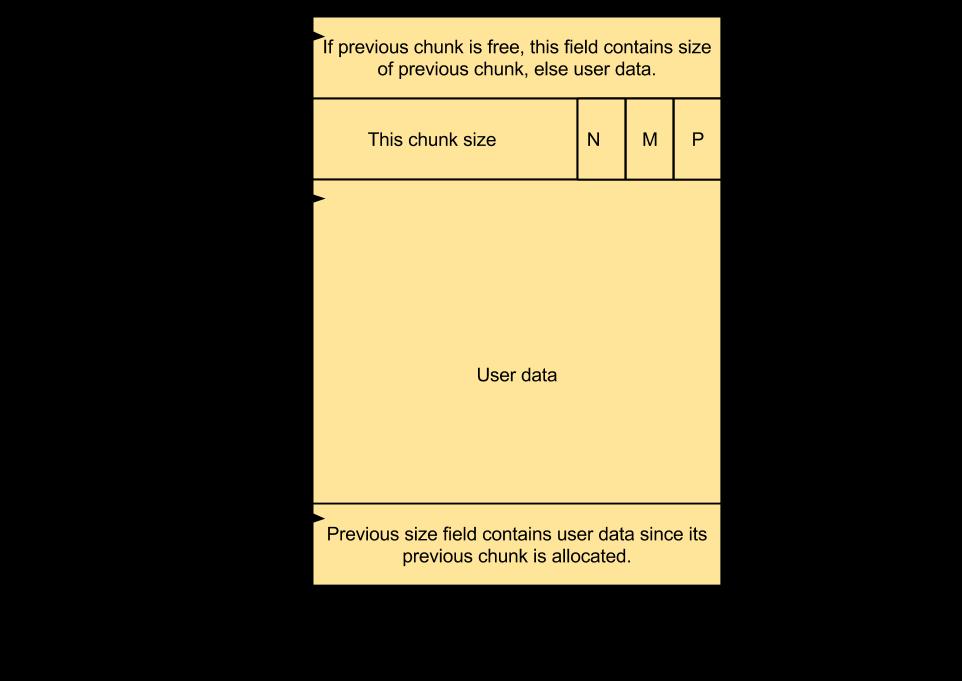
size: 这部分包含了此处 Allocated 块的容量大小,该部分最后 3 bits 包含了关键信息。PREV_INUSE (P)– 这一 bit 在前一个块被分配时就被设置。IS_MMAPPED(M) – 这一 bit 在块即在 mmap 时被设置。NON_MAIN_ARENA(N) – 这一 bit 在块分配给 thread arena 时设置。
注意:
其他 malloc_chunk (比如 fd -- forward point,bk-- back point)的部分不会用于分配块。因此用户数据在这个区域。
由于存储 malloc_chunk 需要一些额外的空间,用户请求的容量大小转换成了可用的大小。转化通过不设置可用容量的最后 3 bits 的方式进行,因此它用于存储关键信息。
Free Chunk(空闲块):
prev_size: 两个空闲块是不能毗连在一起的。当两个块都空闲时,它就会与一个单独的空闲块连接。因此前一个块及当前这个释放的块会被分配,同时 prev_size 包含前一个块的用户数据。size: 这个部分包含有空闲块的 size。fd: 前指针 – 同一容器里指向下一块的指针(不是指向物理内存内的下一块)。 Bins:Bins 是 freelist 数据结构。用以支持 Free Chunk。基于块的大小,有几种可用的 bins:
Fast bin 快速bin Unsorted bin 无序bin Small bin 小bin Large bin 大bin
被用来支持这些 bin 的数据结构有:
fastbinsY: 该数组支持 fast bins bins: 该数组支持 unsorted,small 以及 large 容器。总共 126 个容器被划分为以下几种: Bin 1 – Unsorted bin Bin 2 to Bin 63 – Small bin Bin 64 to Bin 126 – Large bin
Fast Bin: 大小在16到80bytes 的块叫做 fast chunk 。支持 fast chunk 的 bin 叫做 fast bins。在上述的这些 bin 里,fast bins 在内存分配和重新分配上更快。(译者注:只有 fast bin 是 LIFO 其他的 bin 都是 FIFO)
bin 数量 -10
每个 fast bin 包含 free chunk 的一个单向链表。既然在 fast bins 里,在列表中间块不会被移除,单向链接列表被使用。添加和删除都在列表末尾之前进行 - LIFO(后进先出)。
Chunk size –8 bytes apart块大小(size) - 8 bytes 累加
Fast bins 包含大小为 8 bytes 累加的块的 binlist 。即,第一个 fast bin(index 0) 包含 16 bytes 块的binlist,第二个 fast bin (index 1)包含 24 bytes 以此类推……(译者注:binlist 是 bin 的一个链表) 在一个独有的 fast bin 内的块大小是一样的。
在malloc 初始化过程中,最大的 fast bin 的大小设置为64(!80) bytes。因此通过块的默认大小设置为 16 到 64 就可以将其划分为 fast chunks 了。 不能合并 - 空闲的两个块可以相邻,但不能合并为一个空闲块。不能合并导致产生外存储碎片,但它可以大大提速!! malloc(fast chunk) –
初始状态fast bin的最大容积 以及fast bin 目录是空的,因此即使用户请求一个 fast chunk,服务它的是small bin code而不是fast bin code。
之后当它不再为空时,计算fast bin 目录以检索其对应的 binlist。
来自以上被检索 binlist 的第一个块会被移除并返回给用户。
free(fast chunk) –
计算Fast bin 目录以检索其对应的 binlist。 该空闲块被添加到以上检索 binlist 的最前位置。
Unsorted Bin: 当小或者大的块被释放而非把他们添加到各自 bin 里时,它会被添加到 unsorted bin 里。 该途径给了 "glibc malloc" 第二个机会再次利用最近释放的块。因此内存分配以及回收的速度都会有所提升(因为 unsorted bin)由于排除了用于查找合适容器的时间。
Number of bins – 1
Unsorted bin 包含空闲块的一个循环双向链表(也称为 binlist 容器列表)。 块的大小 - 没有大小限制,任何大小的块都属于此容器。
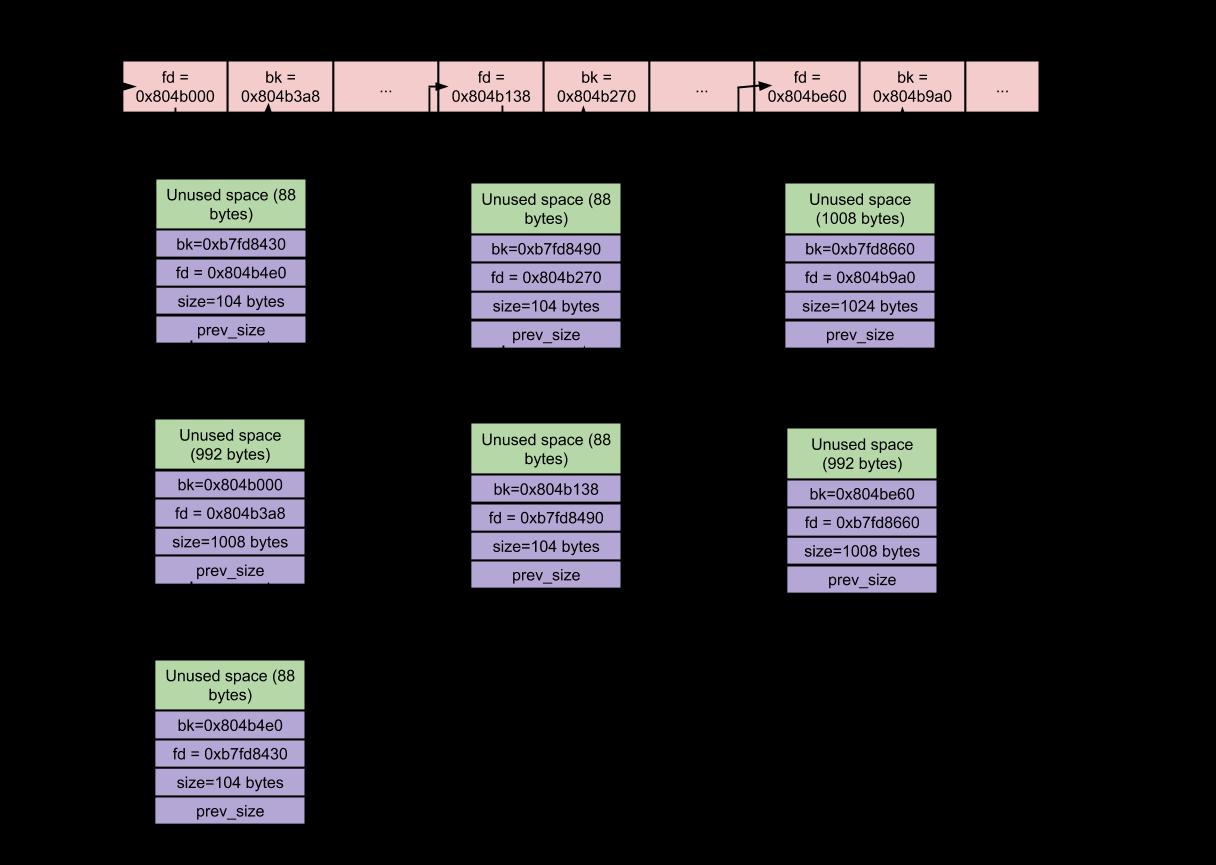
Small Bin: 小于 512 bytes 的块叫做 small chunk。 支持 small chunks 的容器叫做 small bins。 Small bins 在内存分配和回收时比 large bins 快(比 fast bins 慢)。
Number of bins – 62
- 每个 small bin 含有空闲块的一个循环双向链表(也称为 binlist 容器列表)。在 small bins 里, 块从列表中间断开链接后,便使用双向链表。在这里列表头部实现添加并在列表的后部删除 - FIFO(先进先出)。
Chunk Size – 8 bytes 递增
- Small bin 包含一个块大小为 8 bytes 递增(即,第一个 Small Bin(Bin 2)包含块大小为 16 bytes 的binlist,第一个 Small Bin (Bin 3)包含块大小为 24 bytes 的 binlist 以此类推)的 binlist。
- 一个 small bin 里的块大小是一样的,因此不需要分类。
合并 - 空闲的两个块不能毗邻,会被合并为一个空闲块。合并消除了外存储碎片但是运行大大减速!!
malloc(small chunk) – * 初始状态下所有 small bins 都是 NULL,因此即使用户请求一个 small chunk,提供服务的是unsorted bin code而不是small bin code。 * 在第一次调用 malloc 期间,在 malloc_state 里发现的 small bin 和 large bin 数据结构(bins 容器)被初始化(即,bins 会指向它自己表示他们是空的)。 * 之后当 small bin 处于非空状态时,其对应 binlist 中的最后一个块会被移除并返回给用户。 free(small chunk) – * 释放块时,查看其前一个或下一个块是否空闲,如果空闲就合并(即,从他们各自的链表里解除块的链接,然后在unsorted bin的链表最开端添加新的统一的块)。
Large Bin: 大小大于等于 512 bytes 的块称为 large chunk。支持 large chunks 的 bins 叫作 large bins。Large bins 在内存分配和回收中比 small bins 要慢。
Number of bins – 63 每个 large bin 包含空闲块的一个循环双向链表(也称为 binlist )。在 large bins 里,块在任何位置(前端或中间或尾部)被添加或移除后,开始使用双向链表。 这 63 bins 以外:
- 32 bins 包含大小为64 bytes累加的块的 binlist。即,第一个 large bin(Bin 65)包含大小为 512 bytes 到 568 bytes 的块的 binlist,第二个 large bin(Bin 66)包含大小为 576 到 632 bytes 的块的 binlist 以此类推……
- 16 bins 包含着大小为512 bytes累加的块的 binlist。
- 8 bins 包含着大小为4096 bytes累加的块的 binlist。
- 4 bins 包含大小为32768 bytes累加的块的 binlist。
- 2 bins 包含大小为262144 bytes累加的块的 binlist。
- 1 bin 包含一个拥有剩余容量大小的块。
不同于 small bin,在 large bin 里的块大小是不同的。因此他们以降序排列。最大的块在最前端而最小的块被排到 binlist 的末尾。
合并 - 空闲的两个块不能相邻,而是合并为一个空闲块。
malloc(large chunk) –
初始化状态下所有 large bins 都是 NULL,因此即使用户请求一个 large chunk,是下一个最大的 bin code提供服务,而不是large bin code。
同样在第一次调用 malloc 期间,在 malloc_state 里发现的 small bin 和 large bin 数据结构(bins)被初始化。即,bins 会指向它自己表示它们是空的。
此后当 large bin 不为空时,如果最大块的大小(在它的容器列表里)比用户请求的大小还大, binlist 会从尾部到头部,来查找一个大小接近或等于用户请求大小的合适的块。一旦找到,这个块将分裂为两个块。
用户块(拥有用户请求的大小)-返回给用户。
剩余块(拥有剩余容量的大小)-添加到 unsorted bin。
如果最大块的大小(在它的容器列表里)小于用户请求的大小,那么尽量使用下一个最大(非空)bin 为用户的请求提供服务。下一个最大的 bin code 会扫描容器映射来查找下一个最大的非空 bin ,如果找到任何一个,从 binlist 里检索到了一个合适的块,分裂并返回给用户。如果没找到,尝试使用Top Chunk为用户请求提供服务。
free(large chunk) – 它的程序与空闲(small chunk)类似。
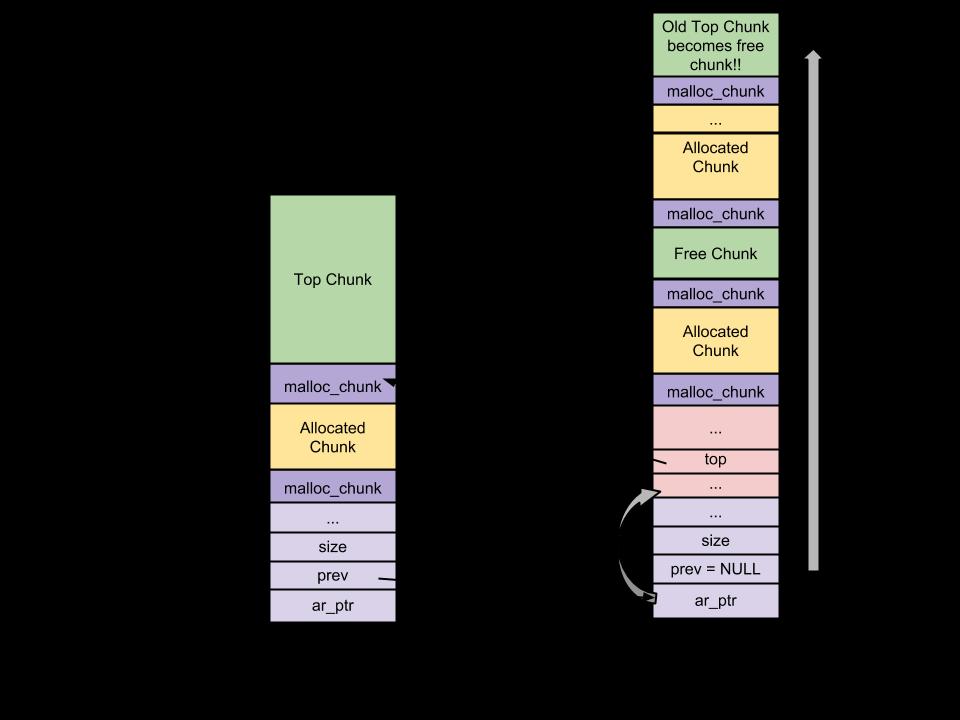
Top Chunk: 在一个 arena 顶部边框的块叫做开始块(Top Chunk)。它不属于任何容器。在任一 bin 里,Top Chunk被用于在没有空闲块时为用户请求提供服务。
用户块(拥有用户请求的大小) 剩余块(拥有剩余容量的大小)
剩余块变成新的顶部。如果开始块大小比用户请求的大小要少,开始块使用sbrk(main arena) 或mmap(thread arena)系统调用来扩展。
最后剩余块:是来自一个小请求的最近一次分裂的剩余。最后剩余块帮助引用地址(即,small chunks 的连续 malloc 请求可能在被分配时结束)彼此间更靠近。
但是除了在一个 arena 里可利用的的众多块,哪些块有资格成为最后剩余块呢?
当一个用户请求 small chunk 时, 不能通过 small bin 以及 unsorted bin 提供服务,这时会扫描 bin 映射会以查找下一个最大(非空)bin 。就像之前所说,一旦找到下一个最大(非空)bin ,它将分裂成两块,用户块返回给用户,同时剩余块添加到 unsorted bin。此外,它会变成新的最后剩余块。
引用地址是怎样归档的?
现在当用户随后请求的一个 small chunk 并且最后剩余块是 unsorted bin 里唯一的块时,最后剩余块会分裂成两块,用户块会返回给用户同时剩余的那个块会添加到 unsorted bin。此外,它还会成为新的一个最后剩余块。如此后续的内存分配会相继结束。
 跳跳糖
跳跳糖
